郯庐断裂带临沂段土壤氢地球化学特征及活动性分析

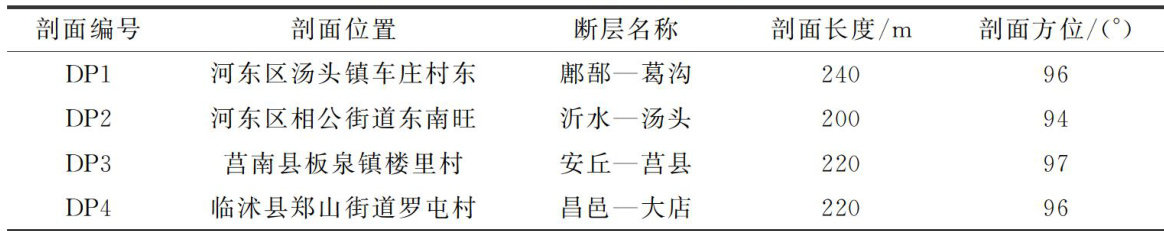
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:P315.72 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1000-0844(2025)06—1416—09
Abstract : Soil radon measurements were conducted across the Linyi segment of the Tan-Lu fault zone to investigate its soil radon geochemical characteristics,major fault activity,and associated environmental impacts. This study employed geochemical parameter statistics, correlation analysis,environmental risk assessment, and fault activity analysis using radon concentration data from the Changyi—Dadian,Anqiu—Juxian, Yishui—Tangtou,and Tangwu—Gegou faults within the Linyi segment. Key findings include the following.(1) The soil radon gas in the Linyi segment of the Tan—Lu fault zone is spatially unevenly distributed,with distinct anomalous intervals.The intensity and extent of these anomalies are clearly controlled by major faults.(2) Correlation analysis shows a strong correlation between soil radon gas and carbon dioxide content,both serving as effective indicators of fault structure activity. (3) Environmental quality assessment reveals that the study area predominantly poses low risk,whereas the vicinity of major faults constitutes high-risk zones. (4) Fault activity analysis ranks the region's major faults in the following descending order of activity: Changyi—Dadian fault, Tangwu—Gegou fault,YishuiTangtou fault,and Anqiu—Juxian fault. This study provides foundational data for disaster prevention and mitigation,earthquake monitoring,and environmental protection in the Linyi segment of the Tan—Lu fault zone.
Keywords: Tan—Lu fault zone; soil; radon;geochemistry;Linyi
0 引言
土壤氢元素是指在土壤中以气体形式存在的放射性元素氡,也是土壤中唯一具有放射性的惰性气体[。(剩余16333字)