EICP溶液改良红层泥岩填料强度及孔隙演化规律研究

打开文本图片集
Abstract: Red mudstone subgrades under wetting-drying cycles frequently suffer from settlement and pavement cracking because of the localized disintegration and softening of fill materials. This study employs enzyme-induced calcium carbonate precipitation (EICP) to modify red mudstone fill material from Gansu Province. Unconfined compressive strength (UCS) tests and crack evolution analysis were conducted on untreated and EICP-treated specimens subjected to wettingdrying cycles. The pore structure of the specimens under wetting-drying cycles was characterized via nuclear magnetic resonance testing, and the curing mechanism was investigated using scanning electron microscopy. Results indicate that the UCS of the specimens is negatively correlated with the cycle number. The EICP-treated specimens under wetting-drying cycles exhibit lower moisture variation rates and reduced dehydration rates than the untreated specimens. Crack ratio and length decrease significantly in the modified specimens. Therefore,EICP can effectively suppress the growth of medium and macropores after wetting-drying cycles. The medium and macropores show an exponential relationship with UCS. This investigation on the mechanical behavior and crack evolution of modified red mudstone fill material under wetting-drying cycles offers critical references for its engineering application in subgrade construction.
Keywords: red mudstone fill material; EICP technology; weting-drying cycles; unconfine( compressive strength;crack;nuclear magnetic resonance
0 引言
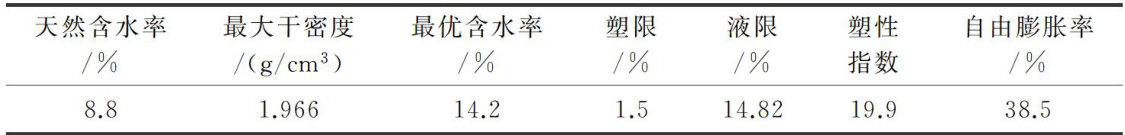
红层泥岩是指外观主色调为红色的碎屑和黏土沉积岩,主要形成于白垩系、侏罗系、三叠系及第三系的陆相沉积[1。(剩余19444字)