空气悬架储气罐数值模拟及研究

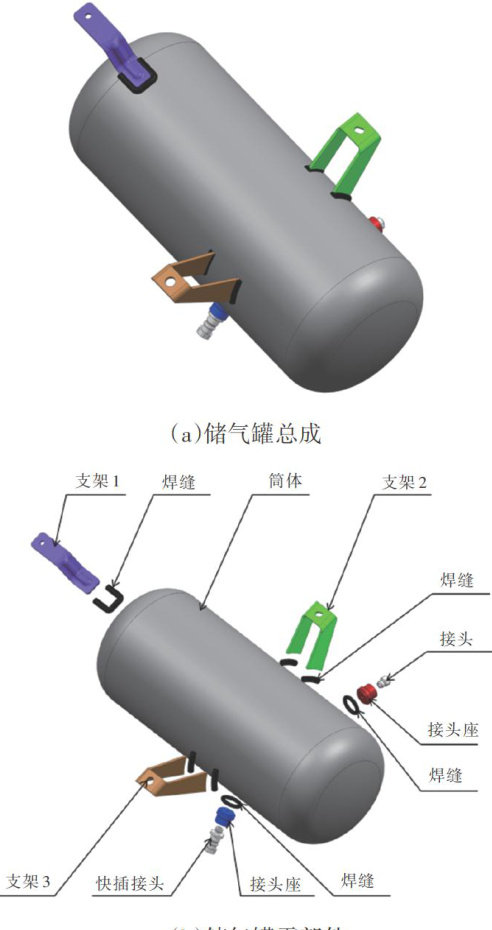
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:TH49 文献标志码:B DOI:10.19710/J.cnki.1003-8817.20250095
Abstract:This study systematicallyinvestigates the pressure-bearing capacity and failure mechanism of air suspensionreservoirs throughnumerical simulation,bursttesting,and theoretical calculation.Basedonnonlinear materialconstitutiverelations,numerical simulationsreveal that when thecylinder wallthickness increases to2.3mm, the maximum equivalent plastic strain reaches 6% ,demonstrating sufficient strength to withstand the design pressure of 6 MPa.Burst tests show theactual pressure-bearing of the2.3 mm thick reservoir reaches 7.29 MPa,with failure consistentlyoccurringatthenozzle-jointarea,corelating perfectlywith high-stresszones identifiedinsimulations. Fracturesurfaces exhibitcontinuous tearing morphology,confirming typical ductilefracturecharacteristics.Comparative theoreticalcalculation indicates themean diameter formulaachieves merely2.2%deviation fromexperimentalresults, significantlyoutperformingthe Faupel formula,thusvalidating itssuperiorityfor burstpresure predictionin thinwalled reservoirs.
Keywords:Airsuspension,Airreservoir,Burstpressure,Numerical simulation
1前言
气弹簧、车身加速度传感器、空气弹簧减振器总成、空气悬架控制器(ElectronicControlUnit,ECU)储气罐、供气系统、分配阀和悬架高度传感器等,集成了底盘系统调校、电子控制和橡胶工艺。(剩余4435字)