内质网应激介导的肝缺血再灌注损伤的分子机制与治疗策略

打开文本图片集
【中图分类号】K658.5 【文献标志码】A
【Abstract}Hepaticischemia-reperfusioninjury(IRI)isapathological phenomenonthatcommonlyoccurs during liversurgeryand transplantation.Itleads toserious tisuedamageandfectsliverfunction.ThemechanismsbehindIIarecomplexinvolvingoxidativestress,itorposdetsisdrltistedoetiold plasmic reticuumstress(ERS)inIRIERSactivatestheeclasicalsignaligpathways,ERK,IE1,andATF6,toughthefolded proteinrespose(UP)iming topreliinarilestorendoplasmictiulumomeostasisndprotectcls.Hwever,iftesrs sponse is excessiveorpersistent,ERScanactivate apoptosis signalingpathways,suchas CHOPandBax/Bak,worsening cellinjury. AdditionallERSisoelyelatedtoercellarstrsesposuchutopagdodatieress,ichjntlyte survivalandathofhepatoces.RegutioofRspecialleetiostagetingtereeUpaays,ssiderd tentialtherapeuticpatwayfoallviating hepaticIRI.Pharmacologicalinterventions,suchas4-phenylbutyriccidandtauocholic acid,and genetherapis,uchasockingoutPERKorIE1,avesopositiveeects inprotectingliverfunctionwileibiing
ERS.Thispaper reviews the mechanism of action of ERS in hepatic IRI,focuses on the specific roles of the three UPR pathwaysand theirpotential as therapeutic targets,and explores the future of relatedtherapeuticstrategies.
【Keywords】endoplasmic reticulum stress;hepatic ischemiareperfusion;unfolded protein response;apoptosis;therapeutic target
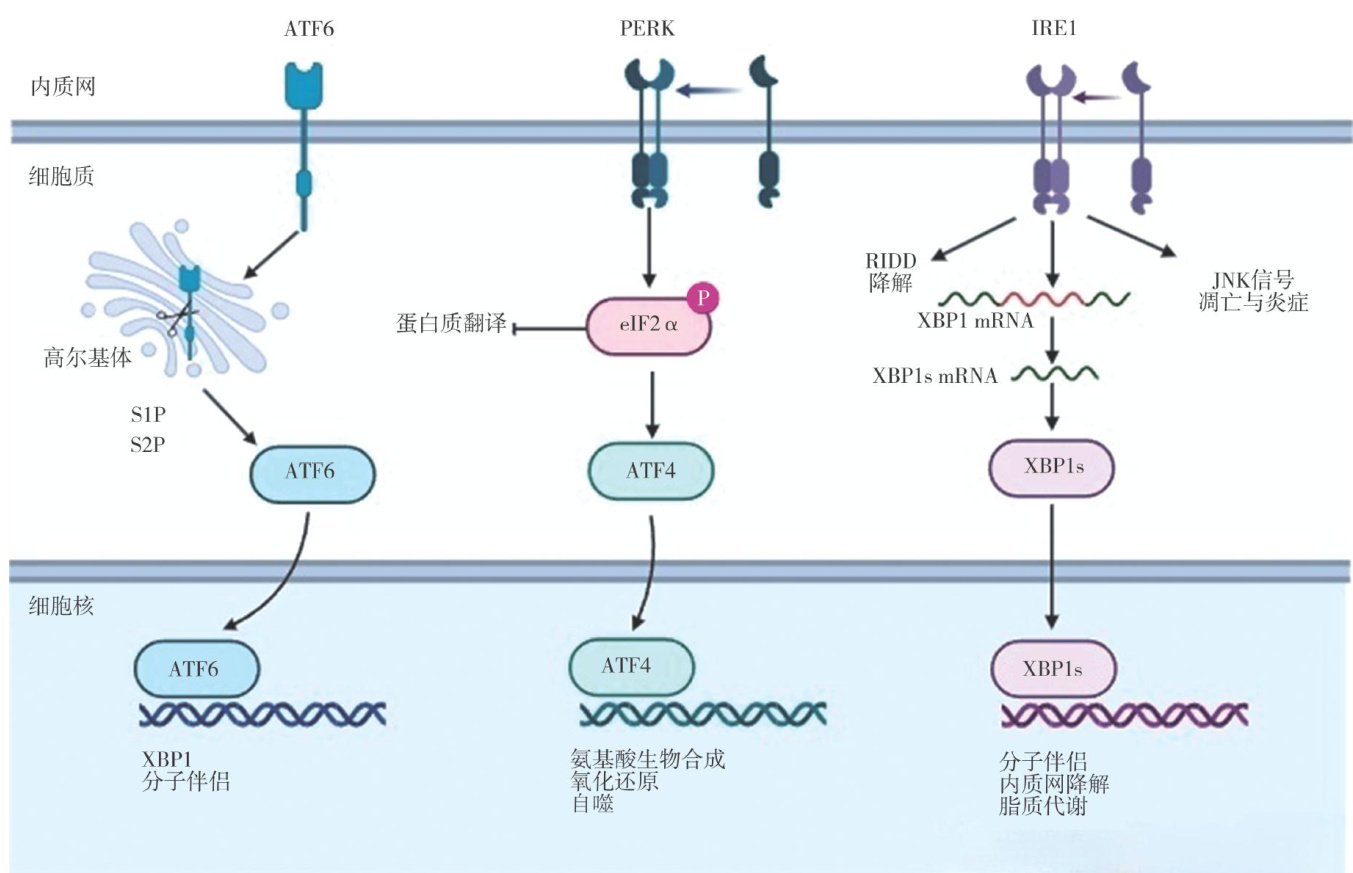
肝缺血再灌注损伤(ischemia-reperfusioninjury,IRI)在肝脏手术、移植和切除过程中普遍存在,是术后并发症和器官功能衰退的主要原因之一。(剩余15512字)