Sp1/ABCA1信号通路在尿毒症动脉粥样硬化中的作用及其调节机制

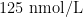
打开文本图片集
【中图分类号】R692【文献标志码】A【收稿日期】2023-09-22
Role of Sp1/ABCA1 signaling pathway in uremic atherosclerosis and itsregulatorymechanism
HuangNingchuan,Ma Hui,Ma Peng
(Departmentof Nephrology,The FirstAfliated HospitalofGuizhou UniversityofTraditional Chinese Medicine) 【AbstractObjective:Toinvestigatetheroleofspecificityprotein1(Sp1)/AT-bindingcasetetransporterA1(ABCA1)sigaling pathwayiuremicatherosclerosisanditsregulatorymechanism.Methods:Mousevascularsmothmusclecels(VSMCs)weredivided into control(Con) group,indophenol sulfate(IS)group,IS + Sp1group,and IS + Sp1+sh-ABCA1 group. The Con group was treated with (20 0.1% DMSO for24h,whileothergroupswere treated with250nmol/LISfor24h.Theprotein expresionofSp1/ABCA1and lipid accumulationwereanalyzedbyWesternblotandDil-labeledoxidizedlow-densitylipoprotein(Dil-ox-LDL)staining.EightyApoE -I- (2 mice were randomlydivided into four groups:sham group,uremia acelerated atherosclerosis(UAAS)group,UAAS+Vector group, andUAS+Sp1 group,with20mice ineach group.Aortic lipids were measuredbyoilredO(ORO)staining.Results:ISpromotedthe fluorescence intensity of intracellular Dil-ox-LDL in a concentration-dependent manner( P <0.05).Compared with the IS group,the IS+Sp1 group had a significantly decreased fluorescence intensity of Dil- ∂⋅0X -LDL( P <0.01).The fluorescence intensity of Dil-ox-LDL inthe IS + Sp1 + sh-ABCA1 group was significantly higher thanthatin the IS+Sp1 group( P <0.05).Compared with the Sham group,the UAAS and UAAS + Vector groups had significantly increased ORO-positive areas in the aorta and aortic root and arch ( P<0.05 ) and sig nificantlyreduced colocation levels of alpha-smoothmuscleactin ( α -SMA)and Sp1intheaortic sinus tissue( P<0.05 ).Compared with the UAAS + Vector group,the UAAS + Sp1 group had significantlyreduced ORO-positiveareasin theaorta and aortic root and arch ( P<0.05 )and significantly increased colocation levelsof α-SMA andSp1( P <0.05). The protein expression levels of Spl and
ABCA1in the aortictisseof the UAAS+Sp1 group were significantly higher than those of the UAAS+Vector group( P <0.05) . Conclusion:UremictoxinISmayinducelipidaccumulationintheVSMCsbyinhibitingtheSpl/ABCAsignalingpathway,thusaelerating endothelial dysfunction in uremia and promoting the progression of atherosclerosis. 【Key words】specificity protein1;ATP-binding cassette transporterA1;uremia;atherosclerosis;lipid
动脉粥样硬化性心血管疾病是尿毒症患者心血管发病率和死亡率的主要原因。(剩余12796字)