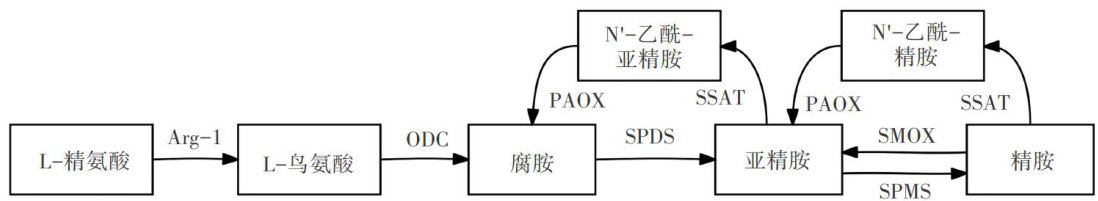
肿瘤微环境内巨噬细胞和T细胞的多胺代谢重编程

打开文本图片集
【中图分类号】R730.3 【文献标志码】A
Metabolic reprogramming of polyamines in macrophages and T cells withinthe tumormicroenvironment
Wang Zhixu,Song Yuxiao,Zhang Bicheng (Cancer Center,Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University)
【AbstractInthetumormicroenvironment(TE),themetabolicreprogrammingofmacropagesandTcelsplaysacriticaloleinthe formationofanimmunosuppresivestateandtumorimmuneescape.Polyamiesarekeysignalingmoleculesandprecursorsforiosynthesis,andthemetabolicstateofpolyaminesprofoundlyregulatethefunctionsof tumorcellandimmunecels.Cytokinesandother substances withintheTMEinducetheexpresionofenzymesrelatedtopolyamine metabolism,drivethemetabolicreprogrammingof polyamines,andthusifluencemacrophageparizationandTcelldiferentiation;meanhile,themetaboliceprogammingofpoly amineseads tothecompetitivedepetionofpolyamieresources witintheTE,promotetumorcelstooptimizeteirmetabolicstrat egiesforsurvivaldvantagesandinhbit thefunctionofimmunecels.erefore,nbitorsofolyaminemetabolismmaybeusedas antitumor drugs by regulating metabolic reprogramming.
【KeywordsItumor microenvironment;macrophages;Tcels;polyamine metabolism;metabolicreprogramming;antitumortherapy
肿瘤微环境(tumormicroenvironment,TME)包含细胞外基质和多种非癌细胞,其中免疫细胞在肿瘤免疫微环境(tumorimmunemicroenvironment,TIME)中扮演关键角色。(剩余12831字)