分化型甲状腺癌患者放射性碘残余消融治疗后涎腺功能评估

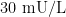
打开文本图片集
Evaluationof salivary gland function inpatientswithdiferentiated thyroid cancerafterradioiodine remnantablation therapy
NiuShuli,ZhangSen,LiuYuhao DepartmentofNuclearMedicine,People's Hospital ofDeyang City,Deyang 618ooo,China
【Abstract】 Objective To evaluate the changes in salivary gland function before and after radioiodine remnantablation(RRA)treatment inpatients with differentiated thyroidcancer(DTC)who have undergone thy-roidectomy.MethodsToensurecomparisonofsali-vary gland function under the same thyroid functional status,we retrospectivelyselected patients who had under-gone two radioiodine(RAI) treatments as subjects.All patients received RAI treatment dose of 3.7GBq.Salivary gland function was quantitatively analyzed through scintigraphy before and afterRRA treatment (oneweek before treat-ment,and6\~27monthspost-treatment,withanaverage in-terval of 11.68 months).Salivary gland imaging examinations were conducted before each RAItreat-ment (TSH>30 mU/L). ResultsThe uptake indexof the right parotid gland before and after RRA treatment was 4.2and3.6,re-spectively, andfortheleftparotid gland,itwas3.8and3.9;fortherightsubmandibulargland,itwas 4.2and4.2,andforthe left submandibular gland,it was3.9and 3.9.The excretion fraction for theright parotid gland was 46% and 49 % and for theleft parotid gland,it was 48% and 48% ; for the right submandibular gland,it was 36% and 37% ,and for the left submandibular gland, it was 33% and 34% .Statistical analysis showed that neither the uptake index nor the excretionfractionof theparotidorsubmandibularglandsreachedstatisticalsignificancebe-foreandafterRRAtreatment ( P >0.05).ConclusionThe most commonly used therapeutic dose of 3.7 GBq for RRA does not significantly affect salivary gland function.
【Key words】Diferentiated thyroid carcinoma;Radioiodine therapy;Salivary gland imaging DOI:10.19522/j.cnki.1671-5098.2025.01.004
2019年中国国家癌症中心根据2015年全国肿瘤流行情况测算出我国甲状腺癌发病数为20.1万,发病率为14.6/10万,在所有恶性肿瘤中位居第7位,在女性恶性肿瘤中位居第4位。(剩余6322字)