水分管理耦合改良剂施用阻控水稻镉累积的机制

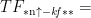
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:X53 文献标识码:A 文章编号: 1000-4440(2025)06-1147-12
Abstract:Cadmium(Cd)contamination poses a severe threat to agricultural production,so effective remediation measures toensurefoodsecurityareurgentlyneeded.Singleremediation strategyis insuffcienttoefectively blocktheuptakeandaccumulationofCd inrice.Therefore,amulti-strategyapproach isrequired.Inthis study,pot experiments were conducted,usingbiochar(BC)andsiliconfertizer(Si)assoilamendmentstoexploretheirefectiveness incontroling
Cd migration and transformation in paddy systems under continuous flooding (CF) and alternate weting and drying (AWD)watermanagement conditions.Theresultsindicated that the CF treatment could increase soil pH and facilitatethetransformation of silicon,andmaintaina lower redoxpotential,therebyit could reduce soil Cd bioavailabilityandensurethesafetyof ricegrainquality.Thecombination of CF with amendments effectively controlled Cd
content,and the CF + BC treatment showed a significant increase in yield.Although AWD treatment increased soil redox potentialandorganicmatercontent,italsoincreasedsoilCdbioavailability,whichwasnotconducivetothecontrolof Cduptake and accumulation in rice.However,the AWD + Sitreatment significantly reduced Cd content in all parts of mature rice plants,decreased Cdaccumulation in rice grains,and increased rice yield compared to the CF treatment.In summary, long-termflooding inregions withabundantwaterresourcescanefectivelyreducegrainCdcontent,butitmaycarraslight risk of yieldreduction,whichcanbe mitigatedbytimelyapplicationof amendments toenhance yield.Inareas with limited waterresources,itisrecommendedtoapplyamendments inconjunction withAWD toensure thesafeproductionof rice.
Key Words: cadmium;rice;water management;biochar;silicon fertilizer;safe production
土壤重金属污染是全球污染面积最大、最严重的环境问题之一。(剩余21489字)