焊接热循环对18CrNiMo钢焊接热影响区 冲击韧度的影响
打开文本图片集
Abstract: During the welding process of bridge steel structures,the temperature effect generated by the welding thermal cycleisacrucial factorleading to microstructural inhomogeneityintheheat-afected zone (HAZ)of welded joints,which may subsequently induce local embritlement and stressconcentration issues in stee structures.This studyutilizes a Gleeble-540thermodynamiccouple testing machine to physically simulate the welding thermal cycle, focusing on analyzing the influence of peak temperature and cooling rate on the microstructure and impact toughness of the HAZof the base material,18CrNiMo steel,used in bridges.The research results indicate that when the peak temperature of the welding thermal cycle exceeds 950°C ,significant austenitic transformation occurs in 18CrNiMo steel during the heating stage,and an increase in peak temperature leads to significant grain coarsening in the HAZ material. During the welding cooling stage,when the t8/5 timeis less than 15s,the martensite content in 18CrNiMo steel increases,resulting ina decrease in impact toughnes.Basedon the above analysis,to effectivelyavoid local embritlement in welded steel structuresof 18CrNiMo,strict interlayer temperaturecontrol during welding and postweld heat treatment measures are necessary.
Keywords:arc welding;heat-affected zone; impact toughness;microstructure
1序言
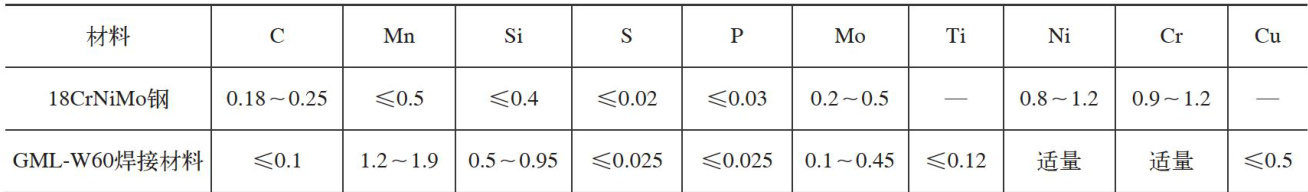
在桥梁工程领域,钢结构因其高强度、良好的韧性和施工便捷性而被广泛应用[1-4]。(剩余5272字)