中国医疗资源供需耦合协调发展的时空演变及其影响因素

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:P936 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1673-5072(2025)05-0525-09
Abstract:Medical and health care is the basic demand of people’s livelihood.Identifying the spatio-temporal characteristics and influencing factors of medical resource supply and demand is significant for testing the equity of health service.By constructing a medical resource supply and demand evaluation system,and combining comprehensive evaluation model,coupling coordination degree model,spatial correlation analysis and geographical detector,this paper discusses the spatio-temporal evolution characteristics and driving factors of medical resource supply and demand in 31 provinces in China from 2O15 to 2021. The results show that:(1)the coupling coordination between supply and demand of medical resources in all provinces shows a slowly rising trend with time,but the gap of inter-provincial medical resource allocation is still expanding,and the provinces with lagging demand account for the highest proportion;(2)the coupling coordination degree is obviously featured by spatial differentiation,gradually forming a“川”gradient development patern with the east as the axis,spreading inland,and showing a“high in the east and low in the west” feature in spatial agglomeration; (3) economic development,population structure,resource agglomeration and government regulation are important driving factors to promote the coupling coordination development between the two,and government regulation with any of other factors together has the strongest explanatory power;(4) according to the results,some suggestions are put forward,such as formulating an efficient and complete regional coordination strategy,constructing the cooperation and exchange mechanism between supply and demand groups,and improving the equity of medical and health expenditure.
Keywords: supply and demand relationship; medical resources;coupling coordination;spatio-temporal evolution; geographic detector
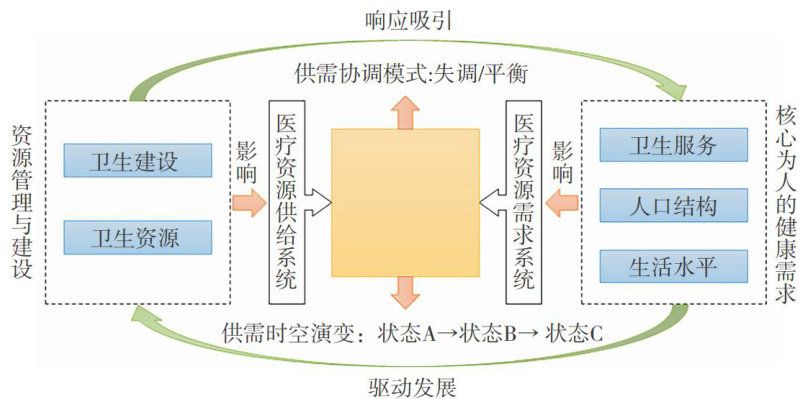
现阶段区域经济、城市人口规模差异塑造了我国卫生服务供给空间差异,地区经济发展表现出明显的核心城市极化趋势[1];与此同时中国人口结构老龄化进程加快,且老龄化问题往往集中于东部发达地区[2],刺激医疗服务需求逐步扩张;紧急公共卫生事件爆发期间患病人数的增加也直接导致医护资源的需求急剧增多[3],这进一步放大了既有资源配置矛盾。(剩余11252字)