基于空间句法和POI数据的寺庙类历史文化街区空间优化研究
——以市大慈寺和文殊院为例

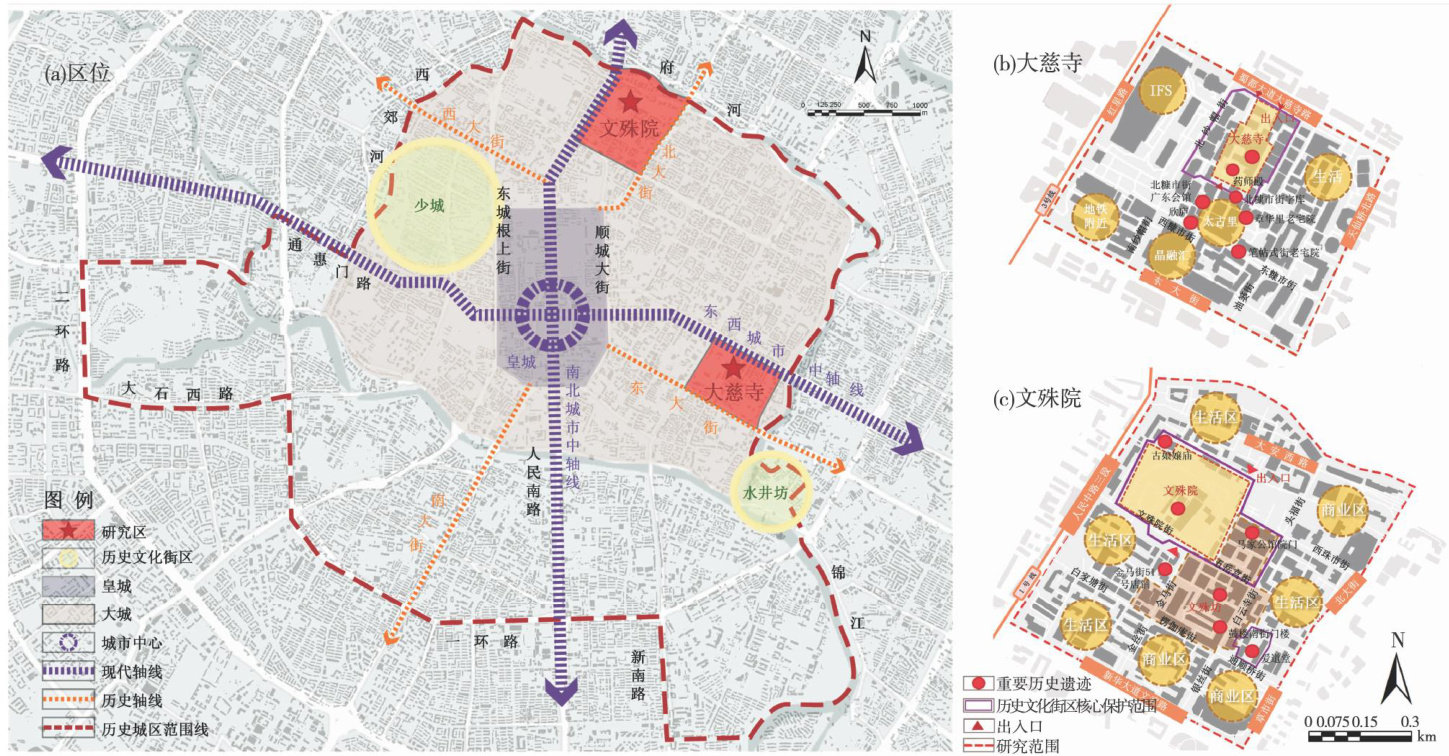
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:TU984 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1673-5072(2025)05-0506-11
Abstract:Temple-centered historical and cultural districts serve as significant carriers of China’s diversified regional cultural heritage.Spatial optimization within these districts facilitates the conservation of cultural heritage,enhances spatial quality and promotes regional tourism development. Based on spatial syntax and POI kernel density coupling analysis,this study explored the spatial characteristics of road structures and tourist service facilities,as well as the correlations between them in the two temple-centered historical and cultural districts of Daci Temple and Wenshu Monastery in Chengdu from the dual dimensions of“space-society”.Subsequently,targeted spatial optimization suggestions were presented to balance the relationships between tradition and modernity,protection and development as well as culture and economy.The results indicate that:(1)The two districts exhibit poor spatial permeability,hindering pedestrians from the interior of the temples,and lack street guidance.Nevertheless,the moderate level of low legibility enhances the exploratory charm in the streets and alleys.(2) The spatial organization of the districts is cohesive,with a clear distinction between primary and secondary areas.Temple culture significantly influences the functional positioning,spatial formation and evolution of the districts.(3) The commercial area surrounding the Daci Temple district exerts a stronger influence than that of the Wenshu Monastery district.Additionally,due to differences in positioning,spatial structure and business distribution,pedestrian flow patterns difer between the two districts at various times.(4)The distribution of various service facilities demonstrates varying degrees of correlation with global integration.The distribution of leisure,shopping and dining facilities shows a higher correlation.Besides accessibility,facility distribution is influenced by additional factors.Based on the comparative analysis,spatial optimization countermeasures are summarized from 4 aspects including street pattern,historical relics,industry distribution and cultural characteristics of the districts,so as to ofer effective references for the protection,inheritance andrenewal of temple-centered historical and cultural districts.
Keywords:historical and cultural district;spatial syntax;Point of Interest (POI) ;temple;spatial optimization ; Chengdu
历史文化街区是动态的城市遗产,随着经济发展与文化保护的矛盾加剧,其面临文化遗存丧失、地块肌理消亡、街区特色同质化等挑战[1-3]。(剩余12615字)