涪江下游浮游生物群落结构、多样性及水质现状研究

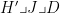
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:Q89 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1673-5072(2025)05-0461-12
Abstract:In order to explore the spatial status of plankton community structure,diversity,and water quality in the lower reaches of the Fu River,18 sampling sites were set up in September 2O23.A survey and an analysis of the plankton status were conducted,and the Shannon-Wiener diversity index ( □edH′ ),Pielou index (J) ,and Margalef index (D) were used to comprehensively evaluate the extent of water pollution. The results show that a total of 195 species of phytoplankton are distributed,belonging to 8 phyla and 74 genera,with Bacillariophyta being the dominant group,accounting for 47.69% . The average density of phytoplankton is 24.23×104 individuals ⋅L-1 , with an average biomass of 2.0814mg⋅L-1 . The average values of H′,J and D are 2.94,0.84,and 7.10,respectively. As for zooplankton,118 species from 53 genera and 4 phyla are recorded,with Rotifera being the dominant group,accounting for 44.07% . The average density and biomass are 39 individuals ·L-1 and 0.0249mg⋅L-1 ,respectively. The average values of H′,J,andD for zooplankton are 2. 6779,0.8740,and 5.1471,respectively. Redundancy analysis indicates that the phytoplankton community structure is primarily influenced by ammonia nitrogen ( NH3 1 N).The assessment of plankton diversity indices suggests that the water pollution levels in diferent sections of the river range from clean to slightly polluted.The results of the physicochemical water quality parameters indicate that the water quality varies from Class I to II,with Class II water in the majority.It is recommended that further monitoring and protection effrts should be strengthened in the ecological management of the water environment in this basin.
Keywords: Fu River; zooplankton ; phytoplankton ; water quality ;diversity
河流生态系统中的物质循环和能量流动与浮游生物密切相关,浮游生物作为食物链的基础环节,在维持水生生态系统平衡中扮演着至关重要的角色[12]。(剩余15210字)