LAC与下腔静脉直径在创伤性休克患者早期诊断中有效性分析

打开文本图片集
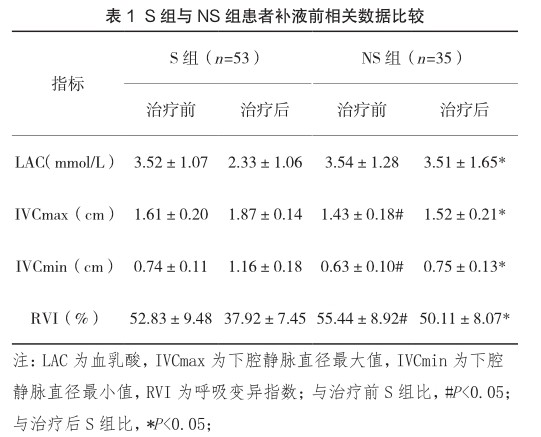
【摘 要】目的:探讨LAC与IVC在创伤性休克患者早期诊断有效性分析。方法:前瞻性队列研究2019年9月—2020年12月于石河子大学第一附属医院就诊的创伤性休克患者88例。根据治疗后是否休克,分为稳定组(S组)和不稳定组(NS组)。采用受试者工作特征曲线及曲线下面积判断各指标的预测意义。结果:治疗前,两组LAC差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);NS组RVI大于S组,IVCmax、IVCmin小于S组,差异有统计学意义(P
【关键词】创伤性休克;下腔静脉直径;乳酸;呼吸变异指数
Effectiveness of LAC and inferior Vena cava diameter in early diagnosis of traumatic shock
CHEN Fanfan1, TAO Siqi1, LI Yajun1, OU Yangjun2
1.Shihezi University, Shihezi Xinjiang 832000, China;2.Emergency Department, First Affiliated Hospital, Shihezi University, Shihezi Xinjiang 832000, China
【Abstract】Objective:To evaluate the efficacy of LAC and IVC in the early diagnosis of traumatic shock. Methods:A prospective cohort study was conducted in 88 patients with traumatic shock from September 2019 to December 2020 in the First Affiliated Hospital of Shihezi University.According to whether there was shock after treatment, they were divided into stable group (S group) and Unstable Group (NS group) . The subject’s working characteristic curve and the area under the curve were used to judge the predictive significance of each index. Results:There was no significant difference in LAC between the two groups before treatment(P>0.05); RVI of NS group was larger than that ofS group, and IVCmax and IVCmin were smaller than those of Sgroup(P
【Key?Words】Traumatic shock; Inferior Vena Cava diameter; Lactic acid;Respiratory variability index
创伤会对机体造成不同程度的损害,创伤性休克是其早期常见的并发症,且是导致创伤患者早期死亡的主要原因之一[1]。(剩余3235字)