重庆市蔬菜基地尾菜资源化利用模式研究

打开文本图片集
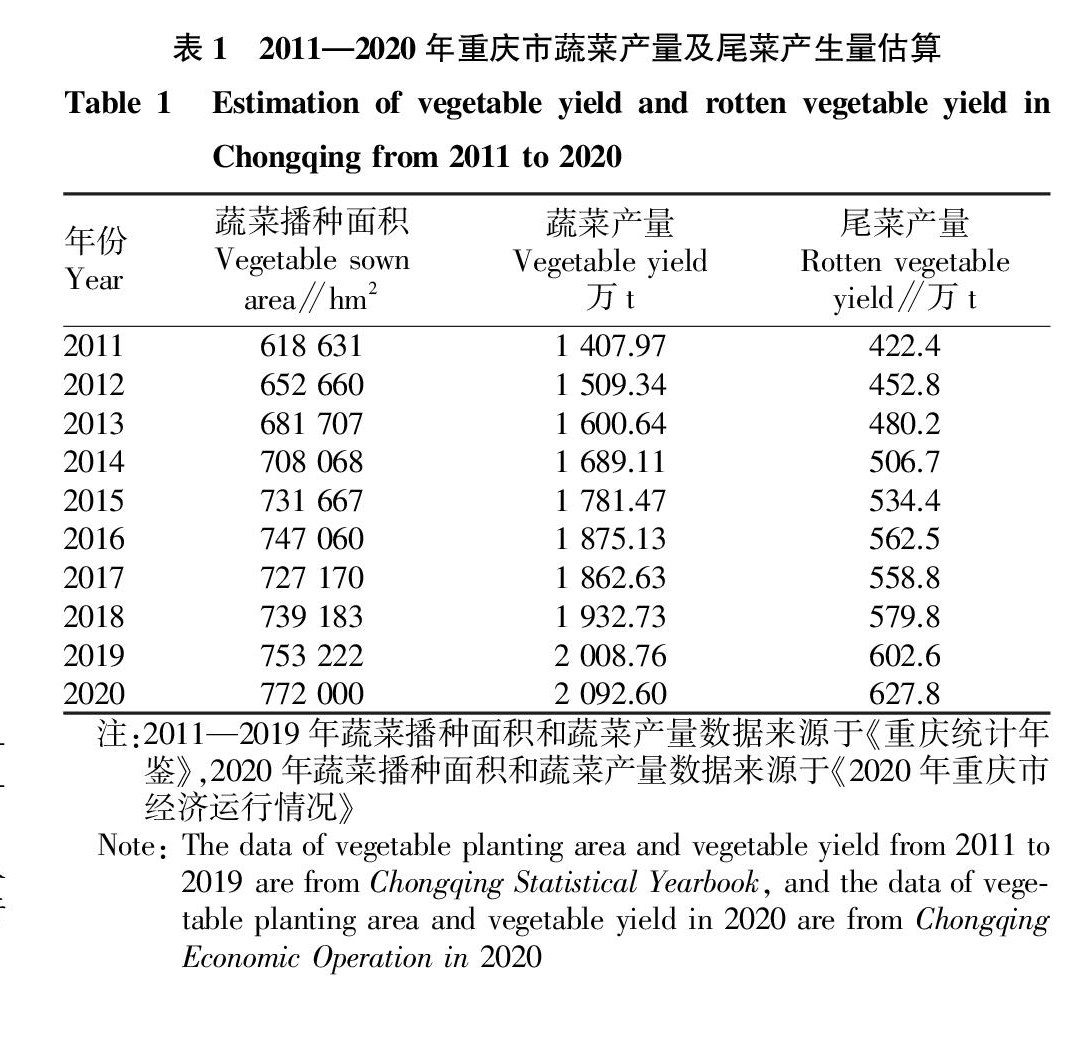
摘要 对重庆市蔬菜尾菜产生量进行了估算及特点分析,并经过调研,总结了肥料化模式、饲料化模式、能源化模式、生态化模式等重庆目前尾菜处理利用模式。同时,也提出了尾菜利用过程中存在的问题及相关建议,为蔬菜基地尾菜资源化利用提供参考。
关键词 尾菜;资源化利用;模式;蔬菜基地
中图分类号 X 71文献标识码 A文章编号 0517-6611(2022)22-0049-03
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2022.22.013
开放科学(资源服务)标识码(OSID):
Study on Resource Utilization Model of Rotten Vegetable in Vegetable Base of Chongqing
WEI Xiu-li 3, LIU Ke 3, XU Jin1 et al
(1. Chongqing Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Chongqing 401329;2. Southern Scientific Observing and Experimental Station for Development and Utilization of Rural Renewable Energy, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Chongqing 401329;3. Chongqing Key Laboratory of Agricultural Waste Resource Utilization Technology and Equipment Research and Development, Chongqing 401329)
Abstract The yield of vegetable rotten vegetables in Chongqing was estimated and its characteristics were analyzed. Through investigation and research, the current treatment and utilization patterns of rotten vegetables in Chongqing such as fertilizer mode, feed mode, energy mode and ecological mode were summarized. At the same time, the problems and relative suggestions in the utilization process of rotten vegetables were put forward, which could provide reference for the resource utilization of rotten vegetables in vegetable base.
Key words Rotten vegetable;Resource utilization;Mode;Vegetable base
重庆市地处长江中上游,位于三峡库区腹心之地,境内山地面积占76%,丘陵占22%,河谷平坝仅占2%;主要河流有长江、嘉陵江、乌江、涪江、綦江、大宁河等,年降水量1 105.5 mm,属亚热带季风性湿润气候,年平均气温在18 ℃左右,年日照时数1 200~1 400 h,冬暖夏热、雨量充沛、温润多阴,是我国西南地区重要的蔬菜生产基地。(剩余6274字)