胆道类器官的构建及应用进展

打开文本图片集
关键词:类器官;胆道疾病;药物筛选;再生医学
中图分类号:R659 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1000-503X(2025)04-0611-10
DOI: 10. 3881/j. issn. 1000-503X.16367
Advances in Construction and Application of Biliary Organoids
LEI Zhongwen1,XIANG Yang²,YANG Yijun²
1 DepartmentofHepatobliaySurgryHaikouAilaedHospitalofCentralSuthUnivesityXiagyaSholofedice,Haikou, (20 2 Haikou Key Laboratory of Clinical Research and Transformation of Digestive Diseases,Haikou 57O208,China
Correspondingauthor:XIANGYang Tel:18876163917,E-mail:xiangyang200611@126.com
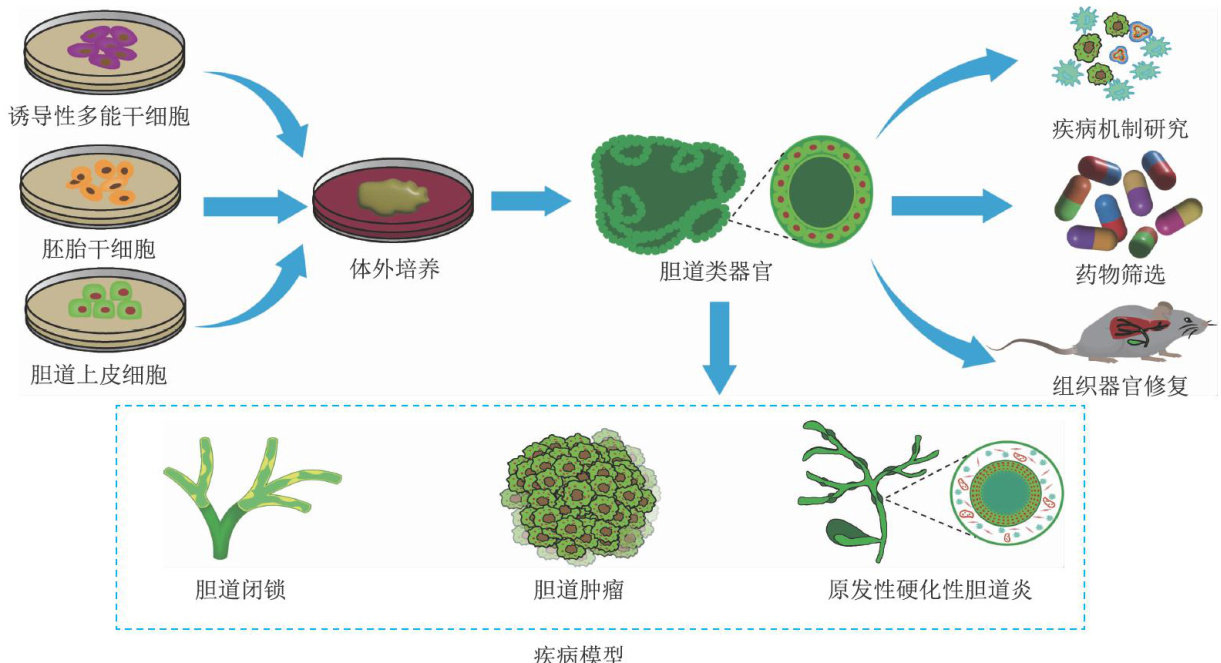
ABSTRACT:Biliary duct injury,congenital biliary atresia,biliary tract tumors, primary sclerosing cholangitis,etc.arecommon and refractory diseases in the digestive system in clinical practice.The existing surgical operations and drug treatments demonstrate limited efects.Organoids,as an emerging technology,have attracted much attention in recent years for deeply understanding the pathogenesis and development ofthese diseases and seeking more effctive treatment approaches.An organoid,a three-dimensional complex derived from stem/ progenitor cells,can simulate the complex structure and physiological function of tissues or organs in vitro. It provides animportant platform for studying the pathogenesis of biliary tractdiseases and brings new hope for the repair andregeneration of biliary tract injury.The seedcells forconstructing biliary organoidsare mainly biliary tract epithelial cells,pluripotent stem cels,etc.The conventional technologies for constructing biliary organoids mainly include embedding,rotary culture,and hanging drop culture.In recent years,new culture technologies such as organ chipand three-dimensional and four-dimensional printing are emerging.This article reviews the construction methods of biliary organoids,discusss the application of these organoids in disease model construction, disease mechanism research,drug screening,and tissue/organ repair,and proposes the current problems and futureresearch directionsof biliaryorganoids,which will provide reference fortreating common refractory digestive system diseases in clinical practice.
Keywords:organoid;biliary tract disease;drug screening;regenerative medicine
ActaAcadMedSin,2025,47(4):611-620
医源性胆道损伤是腹腔镜胆囊切除术最严重的并发症之一,发生率高达 0.4%~1.5% ,可导致胆道狭窄、反复发作胆道炎、继发性胆汁性肝硬化、终末期肝病甚至死亡。(剩余23846字)