气候变化对水体悬浮颗粒物中重金属影响的研究进展

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:X522 文献标志码:A
文章编号:2096-2983(2025)05-0072-09
引文格式:,,,等.气候变化对水体悬浮颗粒物中重金属影响的研究进展[J].有色金属材料与工程,2025, 46(5): 7-80.DOI: 10.13258/jcnki.nmme20250314001.MAOLingchen, ZHANG Bokun,RUAN Yinyan,et al.Research progress onthe impact ofclimate change on heavy metals insuspended particulate mater in aquatic systems[J].Nonferrous Metal Materials and Engineering,2025,46(5): 72-80.
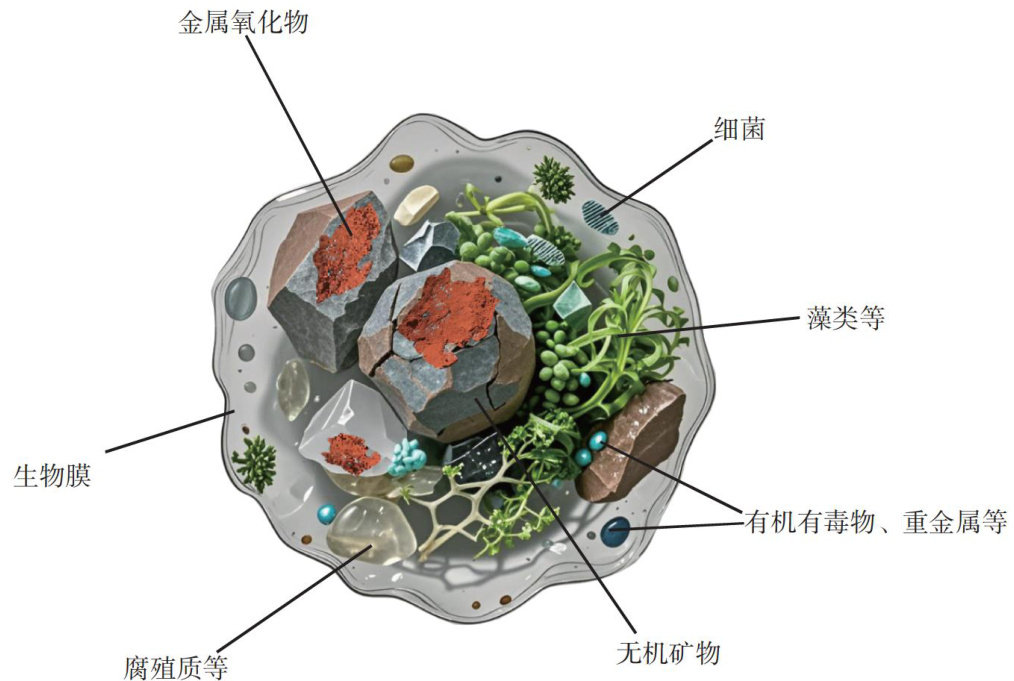
Abstract: Suspended particulate matter (SPM), as a key carrier of heavy metals in aquatic systems, regulates the solid-liquid partitioning of heavy metals through adsorption and flocculation mediated by its inorganic, biological, and organic components. The composition characteristics of SPM,the adsorption-desorption mechanisms of heavy metals on SPM, as well as the chemical speciation and physical fractionation laws have been reviewed. The hydroxyl and carboxyl functional groups on the SPM surface play a dominant role in the environmental behavior of heavy metals through surface complexation and ion exchange has been revealed. Further, the disturbance mechanism of climate change on the dynamic balance of heavy metals in SPM was discussed: the composition evolution of SPM and the changes in water body physical and chemical properties can alter the existing forms of heavy metals, thereby affecting their ecological risks. Future research should integrate artificial intelligence and multi-source data technologies to quantify the cumulative effects of extreme climate events,enhance the precision of risk prediction and provide scientific support for aquatic environment security.
Keywords: suspended particulate matter; heterogeneity; climate change; heavy metal chemicalspeciation
人类活动释放的重金属(如铜、锌、铅、镉、铬、汞等)通过废水排放(电镀、纺织工业废水)含重金属气溶胶的大气干湿沉降及固体废弃物淋滤(冶金废渣、垃圾填埋场)等途径进入水体。(剩余18850字)