多种碰撞工况下的中国与西方体征驾驶员响应对比分析

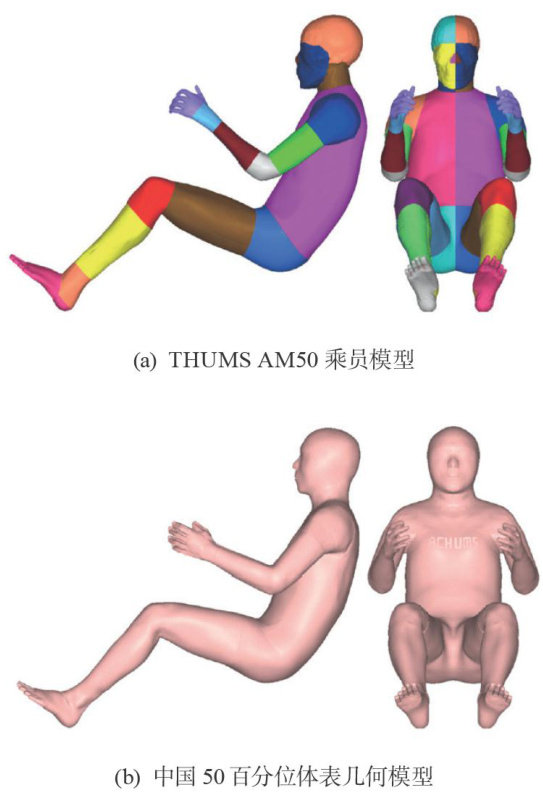
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:U461.91 文献标识码:A DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-8484.2025.03.003
Abstract:A finite element (FE) occupant model of Chinese 50% male was developed to fully understand thediferences in response to impact loading between Chinese and Western,based on theexisting occupant model in Western 50% size and the geometric scaling of the body surface of a Chinese 50% male volunteer. Simulations were conducted under4collsionconditions:the SOB (smalloverlap barrier),the MPDB (mobile progressive deformablebarrer),theFRB(fullwidth rigid barrier)and the FarSide byusing thesubsystemmodel of occupant compartment and the FE human body models (HBM).Diferences in kinematic,dynamic,and biomechanical responses of the Chinese and the Western 50% male drivers under typical collsion conditions were compared and analyzed. Compared with the response of Western 50% HBM,the HIC (head injury criteria) values of Chinese 50% HBM under SOB and FRB conditions are 15.48% and 26.2% lower,while the HIC value in MPDB case is 50% higher;in FRB case,the Chinese 50% HBM has a chest compression rate 31.44% lower,butexhibitshigherribstrain;Themaximum lateraldisplacementof the headunderFarSideconditions is similar,but the Chinese 50% HBM has a significantly lower brain strain,and the lateral shear/axial force on the neck and chest compression rate of the Chinese 50% HBM are lower more than 20% .Therefore,the vehicle restraintsystems designed forwesterner mightbe dificult toachieveoptimal protection for Chinese people.
Keywords:vehiclesafety;vehiclecolisions;driver response;anthropometric diffrences; human body models
碰撞试验和数值仿真是车辆安全领域主流研究方法,其中采用的研究工具主要为机械假人及其数值模型。(剩余11314字)