基于网络药理学探讨人参皂苷 Rgl 治疗心血管疾病的作用机制

打开文本图片集
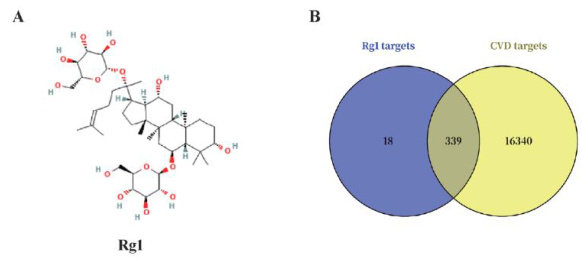
【Abstract】This study investigated the potential mechanisms of ginsenoside Rgl incardiovascular disease (CVD)using networkpharmacologyandmoleculardockingapproaches.Through database screening,weidentifiedcommon targetsof Rgland CVD,constructeda protein-protein interaction (PPI) network for target analysis,and performed moleculardocking betweencoretargetsandRg1.Theresultsshowed339overlappingtargetsbetweenRglandCVD,withcoretargetsidentified throughPPInetwork analysis.Gene Ontology(GO)enrichment yielded1,062 terms,comprising234 molecularfunctions, 725 biological processes,and 103 celllar components.Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichmentinvolvedsignalingpathwaysincludingPathwaysinCancer,ProteoglycansinCancer,EGFRTyrosineKinase InhibitorResistance,andthePhosphatidylinositol3-Kinase(PI3K)/AktSignalingPathway.Moleculardockingconfirmed stable binding interactions between Rg1 andcore target proteins (STAT3,ALB,AKT1,HSP90AA1,EGFR,andSRC). In conclusion,Rgl may interact with these targets to exert preventiveand therapeuticefects on CVD.Thisstudyprovides theoreticalsupport for further research into the mechanism ofRgl againstCVDand clinical drug development.
Key words】 ginsenoside Rg1; cardiovascular disease; network pharmacology; molecular docking[中图分类号]S512.1 [文献标识码]A [文章编号]1674-3229(2025)03-0108-05
0 引言
心血管疾病(Cardiovasculardisease,CVD)是指影响心脏和血管系统的一类疾病的统称,主要包括冠心病、卒中、心肌梗死以及动脉粥样硬化等不同类型。(剩余7413字)