儿童时期恒牙釉质显微硬度及微观结构研究

打开文本图片集
[中图分类号] R788[文献标志码] A [doi] 10.7518/hxkq.2025.2025161
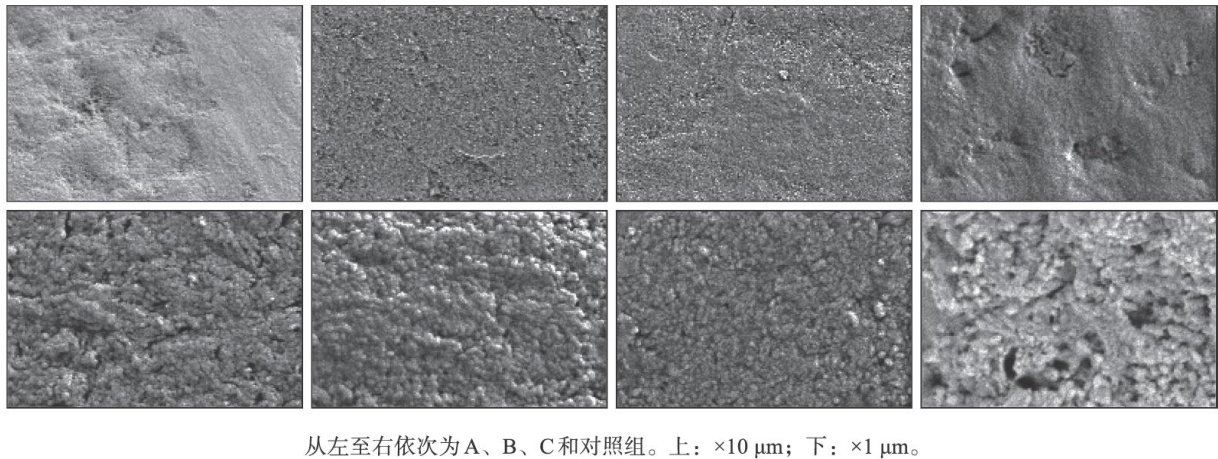
[Abstract]ObjectiveThrough the investigationofthe microhardnessand microstructure of permanent tooth enamel at various eruption stages duringchildhood,this research ofers references fortheearly preventionofchildhood dental caries.MethodsForty-five premolars extracted duetoorthodonticreasons werecollctedand screened.These premolars were divided into three experimental groups according to the time since eruption: Group A(erupted forO-1year), GroupB(eruptedfor1-3years),andGroupC(eruptedfor3-5years).Additionally,thethirdmolarsthat wereextracted due to impactionandhadnot erupted were selectedasthecontrol group,with15teth ineach group.Samples were prepared,and thesurface microhardness,microstructure,and elemental compositionof theenamel were measured using Vickers microhardness tester,scanning electron microscope,and electron probe,respectively.ResultsCompared with thatinthecontrolgroup,themicrohardnessofenamelingroupsA,B,andCincreasedwithprolongederuptiontime,the surface porosity structure decreased considerably,the contents ofNaand Mg on the surface decreased,and that ofF increased (P<0.05) .ConclusionThe microhardness and microstructure of enamel in permanent teeth at different stages vary.Permanent teth areatasubstantially higherriskofcarieswithinoneyearafter eruption,andearly prevention should be emphasized.
[Key words] children; immature permanent teeth;enamel; post-eruptive maturation; microstructure
釉质是牙齿最外层的坚硬结构,主要由羟磷灰石晶体构成。(剩余10678字)