长期卧床老年病人坠积性肺炎发生风险预测模型的构建

打开文本图片集
Construction of risk prediction model for the occurrence of hypostatic pneumonia in long⁃term bedridden elderly patients
ZHANG Ziwei, GUO Siyu, ZHAO Tianxue
Beijing Friendship Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100050 China
Corresponding Author ZHANG Ziwei, E⁃mail: leesay23@21cn.com
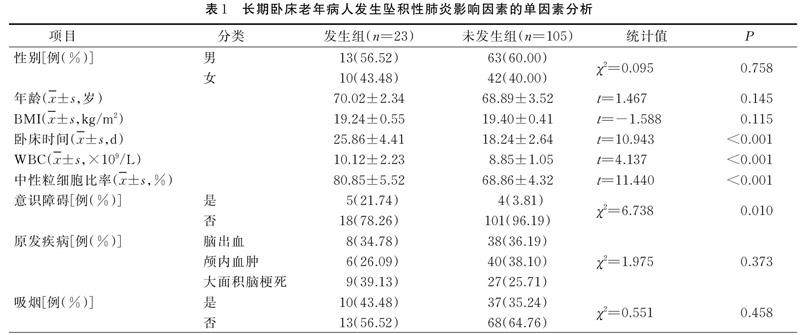
Abstract Objective:To explore the influencing factors of hypostatic pneumonia in long⁃term bedridden elderly patients,and to construct Nomogram model.Methods:A total of 130 long⁃term bedridden elderly patients with hypostatic pneumonia in our hospital were selected as research subjects from January 2018 to January 2022.A self⁃made general data survey questionnaire was used to investigate the patients.Logistic regression equation was used to screen for the influencing factors of hypostatic pneumonia in long⁃term bedridden elderly patients,and Nomogram model was constructed.Results:The incidence of hypostatic pneumonia in long⁃term bedridden elderly patients was 17.97%.Logistic regression analysis showed that bedtime,white blood cell count,neutrophil ratio,occurrence of consciousness disorders,prophylactic use of antibiotics,and swallowing disorders were the influencing factors for the occurrence of hypostatic pneumonia in long⁃term bedridden elderly patients(P<0.05).The average absolute error of internal validation of Nomogram model based on the above influencing factors was 0.002.The model had clinical practical value in the high risk threshold range,and the net benefit of patients was high.Conclusions:The risk prediction model for the occurrence of hypostatic pneumonia in long⁃term bedridden elderly patients has good clinical utility.
Keywords long⁃term bedridden; the elderly; hypostatic pneumonia; influencing factors; risk prediction; Nomogram model; nursing
摘要 目的:探讨长期卧床老年病人发生坠积性肺炎的影响因素,并构建Nomogram模型。(剩余8852字)