河北平泉地热异常区氟分布特征及成因机制

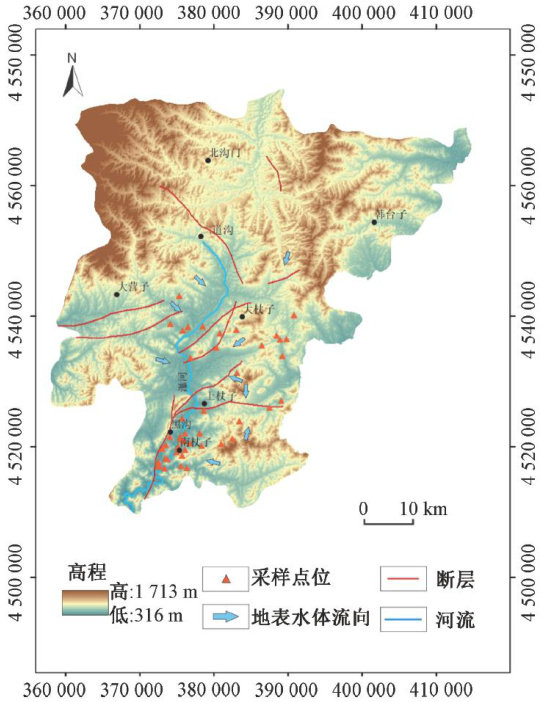
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:P595 文献标识码:文献编码:A 文章编号:2097-5465(2025)03-0081-08
1.The Fifth Geological Brigade of Hebei Bureau of Geology andMineral Resources,Tangshan O630o0,China;2.Hebei Jidong Construction Engineering Co.,Ltd,Tangshan O630o0,China;3.Hebei GEO University,Shijiazhuang050031,China;4.Hebei Center for Ecologicaland Environmental Geology Research,Shjiazhuang O5o031,China
Abstract:Thispaper takesthePingquangeothermalanomalyareaastheresearchobject.Bycolectingandanalyzing48 groundwatersamples,theconcentrationsofmultipleionsincludingfluorideweredetermined.Combinedwiththefluorideion concentrationdistributionmap,temperaturefielddistributionmap,Pipertrilineardiagram,Gibbsdiagram,etc.,the hydrochemicalcharacteristicsofgoundwater,thespatialdistributioncharacteristcsoffuordeionsandtheifomationmsms were systematicall analyzed.The research found that the groundwater chemical type in the study area is mainly HCO3 -Ca ⋅Mg type.Thegroundwaterissignificantlyafectedbywater-rock interactionandevaporationconcentrationproceses.Themaximum fluoride ion concentration is 2.35mg/L and the minimum is 0.13mg/L ,showing a spatial distribution characteristic of being higherinthesouthandlowerinthenorth.Thehigh-fluorideareasarehighlyconsistentwiththehigh-temperatureareasandthe areas withdensefaultdistribution,indicatingthattheupwardmovementofdeepgeothermalfluidsalongfaultsandgeothermal activitiesare thekey factorsforthe increasein fluorideionconcentration.
Keywords:fluoride ion;water chemistry;geothermal resources;genesis mechanism;Pingqua
来稿日期:2025-01-27 DOI:10.13937/j.cnki.hbdzdxxb.2025.03.011
基金项目:河北省专项勘查项目(13000024P00F2D410449K)
作者简介:孙双振(1984—),男,河北保定人,高级工程师,研究方向为水化学和地热地质。(剩余8401字)