藏北地区适宜种植的6种饲草品质分析

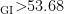
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:S546 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1007-0435(2025)05-1458-07
Abstract:Forage scarcity constitutes a critical botleneck for livestock husbandry development in the northern Tibet,where establishing high-quality,productive artificial grasslands is recognized as a pivotal solution. This study systematically evaluated six high-yield forages previously screened for artificical grasslands establishment in Nagqu (Auena satiua, Triticum secale, Brassca rapa,Brasica napus,Elymus sibiricus and Elymus nutans),using near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy (NIRS)to assessthe nutritional parameters of dry forages and comprehensively evaluating the forage quality of them through grading index (GI).Results demonstrated that four annual forages exhibited crude protein(CP)content of 10.45% to 17.99% ,neutral detergent fiber (NDF)content ranged from 34.03% to 65.76% ,acid detergent fiber(ADF)content ranged from 27.23% to 41.52% ,and GI values ranged from 1O.63 to 86.85. Meanwhile,CP had a strong positive correlation with GI,while fiber(e.g.,NDF and ADF) content had a negative corelation with GI. Allsix species met or exceeded fourth grade forage standards ( GI>6.28MJ) ,with B :rapa achieving premium-grade classification ( ⋅GI>53.68MJ) . Superior performance in total energy content,mineral content,and palatability positions B rapa as the optimal candidate for regional promotion in the northern Tibet.
Key words:Nagqu region;Nutritional value ;Forage quality;Near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy technology; Grading index
西藏是我国畜牧业生产的重要基地,但由于自然条件相对恶劣,天然草地产草量低,饲草短缺严重制约了该地区畜牧业的发展[1-2]。(剩余9785字)