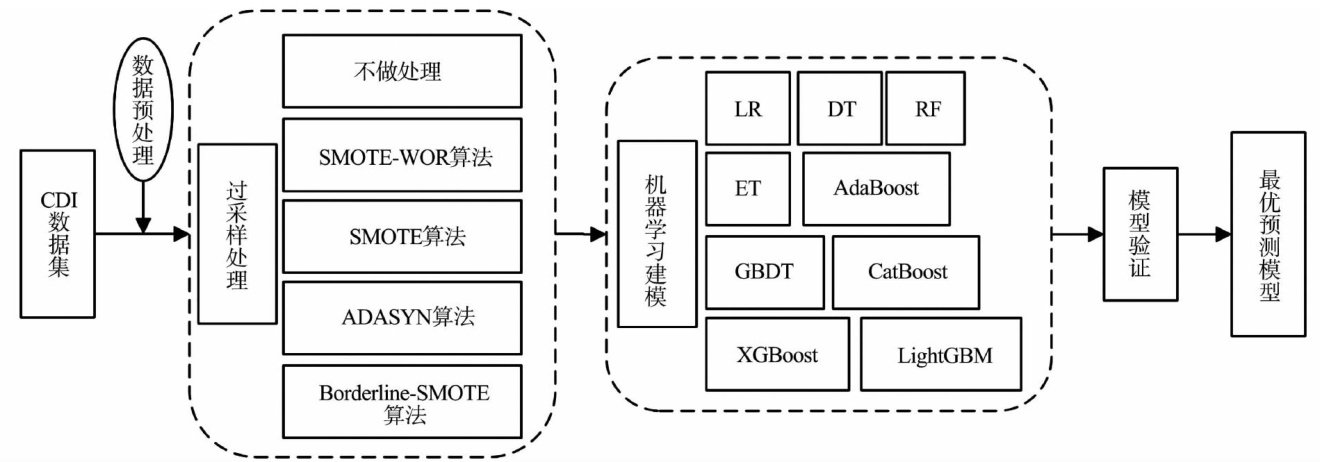
数据不均衡下艰难梭菌感染 预测模型的构建

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:R516;TP181 文献标志码:A 文章编号: 1000-5013(2025)06-0694-09
Abstract:This study utilizes data from critically illpatients in the MIMIC intensive care database to predict the risk of clostridium dificile infection.To addressthe data imbalance in the dataset,a risk prediction method based on improved SMOTE algorithm and machine learning is proposed. First,the improved SMOTE algorithm is enhanced to generate a balanced dataset by incorporating feature weights derived fromodds ratios-an epidemiologically relevant metric-to refine the selection of nearest neighbors.Additionally,to prevent the structural damage of discrete features in the synthesized samples,the sample synthesis method within SMOTE is also modified. Subsequently, multiple machine learning algorithms are used to construct risk prediction models for Clostridium difficile infection in criticallyill patients,respectively. The results show that the model established by the improved SMOTE algorithm and the CatBoost classifiier obtains better predictive performance. Specifically,it achieves an area under the curve (AUC)of 0.75 and a recallrate of O.69 on the test set, and an AUC of O.73 with a recall of O.57 on the validation set.
Keywords: Clostridium diffcile infection;risk prediction model;imbalanced data;SMOTE algorithm;machine learning
艰难梭菌感染(Clostridium dificile infection,CDI)是最常见的医院获得性感染之一,其症状表现为腹泻、暴发性结肠炎、败血症及休克死亡,已被美国疾控中心列为紧急公共卫生威胁[-3]。(剩余12273字)