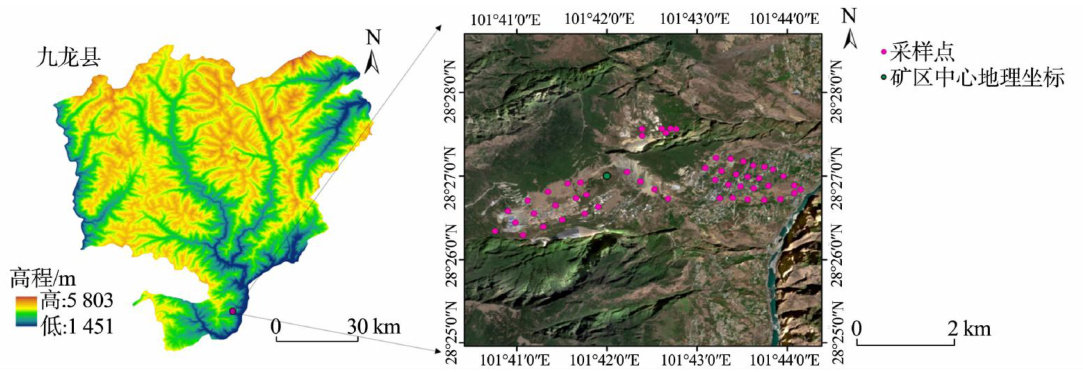
采用高光谱技术的川西矿区周边土壤铬含量反演模型

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:X53(271) 文献标志码:A 文章编号: 1000-5013(2025)04-0462-08
Inversion Model of Soil Cr Content Around Western Sichuan Mining Area Using Hyperspectral Technology
WANG Guangyu1 , YANG Bin1,2,3, WEI Tianyi 1 ,ZHUO Sijie1,CHEN Zhuoer¹,SHA Yingchao1
of Environment and Resource,Southwest University of Science and Technology,Mianyang 621olo,China;2. Mianyang Science and Technology City Division,National Remote Sensing Center of China, Southwest University of Science and Technology,Mianyang 621o1o,China;3.Sichuan Tianfu New Area Innovation Research Institute, Southwest University of Science and Technology,Chengdu 61o299,China)
Abstract:To rapidly detect heavy metals pollution in the soil around caused bymineral resource exploitation and transportation,the soil around the copper mine in western Sichuan was taken as the research object. The original spectral reflectance was processed by fractional-order differentiation from O to1(an interval of 0.2), and the minimum absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) algorithm was used to screen the characteristic bands of the transformed spectrum. Inversion models of Cr content(mass ratio)were constructed using ridge regression,support vector regression,adaptive boosting algorithm, back propagation neural network,and gated recurrent unit (GRU) algorithms. The research results showed that,compared to the original spectra,the maximum correlation coefficient increased by 5% and 9% respectively after O. 2-order and O.4-orderdifferentiation,and the selected feature bands were concentrated in the near-infrared spectral region. The best prediction model was O.4 GRU with determination coeficients of O.799 2,root mean squared error of 4.875 O,and residual predictive deviation of 2.3Oo. This model could accurately predict soil Cr content.
Keywords: soil;western Sichuan mining area; Cr content;spectroscopy analysis;hyperspectral inversion;
fractional-order differentiation;
土壤作为陆地生态系统的重要组成部分,与生态系统其他部分不断循环转化[1]。(剩余10730字)