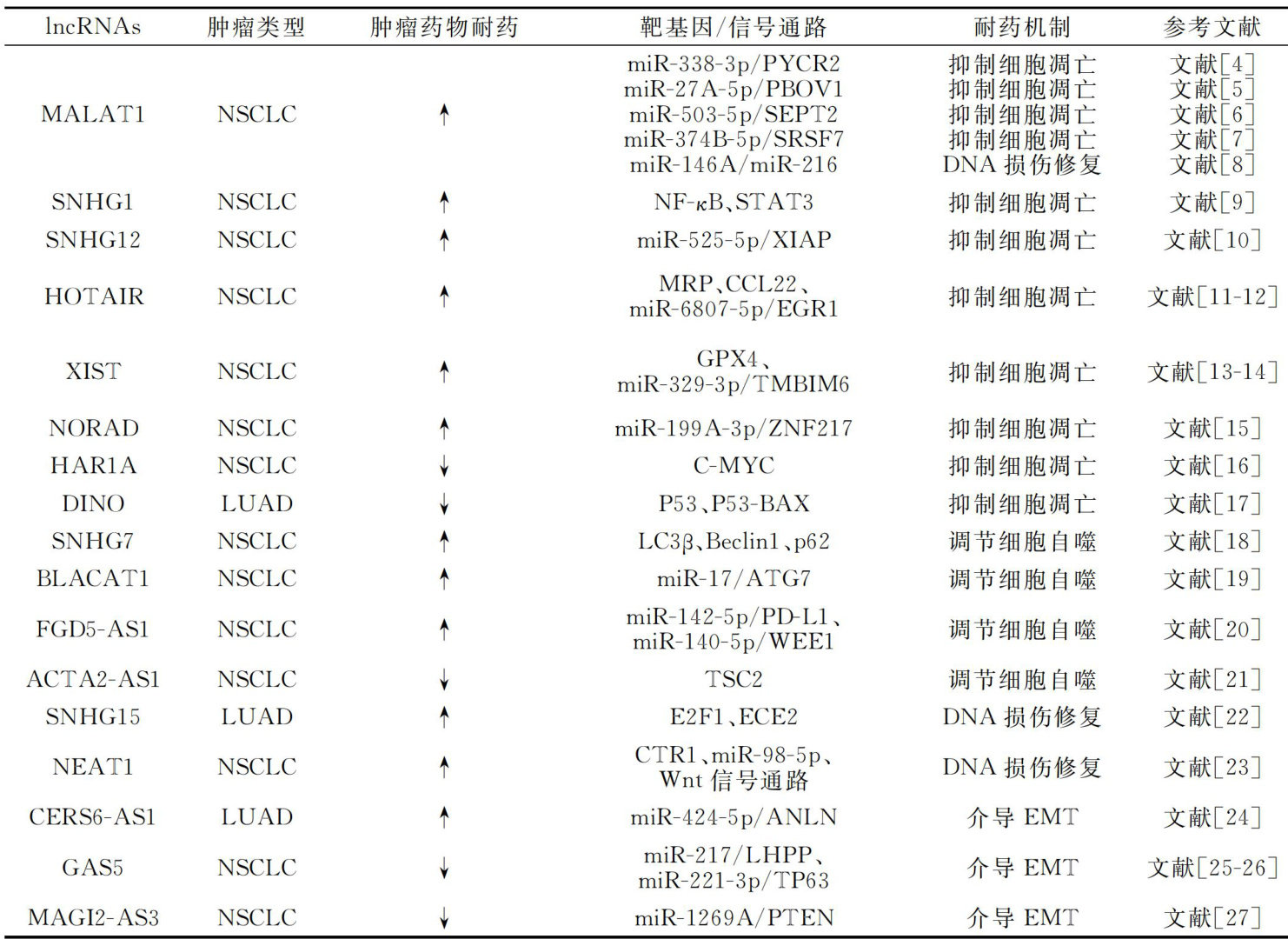
参与肺癌靶向耐药的IncRNAs的作用及其机制

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:R979.1;R966 文献标志码:A 文章编号: 1000-5013(2025)04-0369-10
Role of LncRNAs in Targeted Drug Resistance in Lung Cancer and Their Mechanisms
YANG Suxin 1,2 ,MA
(1.School of Medicine,Huaqiao University,Xiamen 36lo21,China; 2.School of Sociology,Universidad 28o4o,Spain)
Abstract:The roles and mechanisms of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) involved in targeted drug resistance in lung cancer were analyzed comprehensively,elucidating multiple biomarkers for treating lung cancer resistance.By reviewing relevant literature in recent years,the involvement in cisplatin (DDP)resistance in lung cancer,targeted epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs)resistance,targeted anaplastic lymphoma kinase tyrosine kinase inhibitors (ALK-TKIs) resistance,and various long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) resistant to immunotherapy were summarized,and its role and contribution in reversing drug resistance in lung cancer were analyzed. The results show that among the lncRNAs associated with EGFR-TKIs targeted resistance,LINCo046O not only regulates gefitinib resistance through activation of the miR-338-3p/SMC4 pathway, but also plays a crucial role in resistance to osimertinib. Additionally,lung adenocarcinoma metastasis-associated transcript 1 has been shown to affect immune resistance by modulating the expression of major histocompatibility complex proteins and programmed death-ligand 1,highlighting its potential as a key therapeutic target for improving the outcomes of immunotherapy in lung cancer.
Keywords:long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs); lung cancer; cisplatin resistance; targeted drug resistance;molecular mechanism
虽然肺癌化疗和靶向治疗研究已经取得了突破性进展,并显著地改善了患者预后,但肿瘤多药耐药(multi-drug resistance,MDR)导致的化疗失败和复发依旧是肺癌治疗中的一大难题。(剩余20964字)