植物病原真菌聚酮类次级代谢产物研究进展

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:S432.1;S763 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1000-2006(2025)04-0285-08
Abstract:During host-pathogen interaction,pathogenic fungi facilitate host invasionandpathogenesis throughthe productionof secondary metabolites.Fungal polyketides,catalyzed by polyketide synthase(PKS),representthe most abundantclassof bioactivemetabolitesinfungi,theycanestablishphytopathogenic fungi succesful infections,by synthesizing keypigments,virulence factors,and mycotoxins to evade and disrupt hostplant immune mechanisms.This reviewsystematicallyexamines thestructural characteristics,clasification,biological functions,and metabolic regulation offungal typeIPKS.Furthermore,we highlight recent advances in characterizing polyketide compounds and theirbiosyntheticgeneclusters inplant-pathogenic fungi.Potential futureresearchdirectionsforfungalpolyketidesare prospected,with emphasisontheirrole infungal pathogenicity.Collctively,thisworkaims toprovidenovelinsightsand methodologicalframeworksfor elucidatingpathogenicmechanismsoffungal infectionsanddeveloping targeteddisease control strategies.
Keywords:filamentous fungi;polyketide;gene cluster;pathogenic function;regulation mechanism
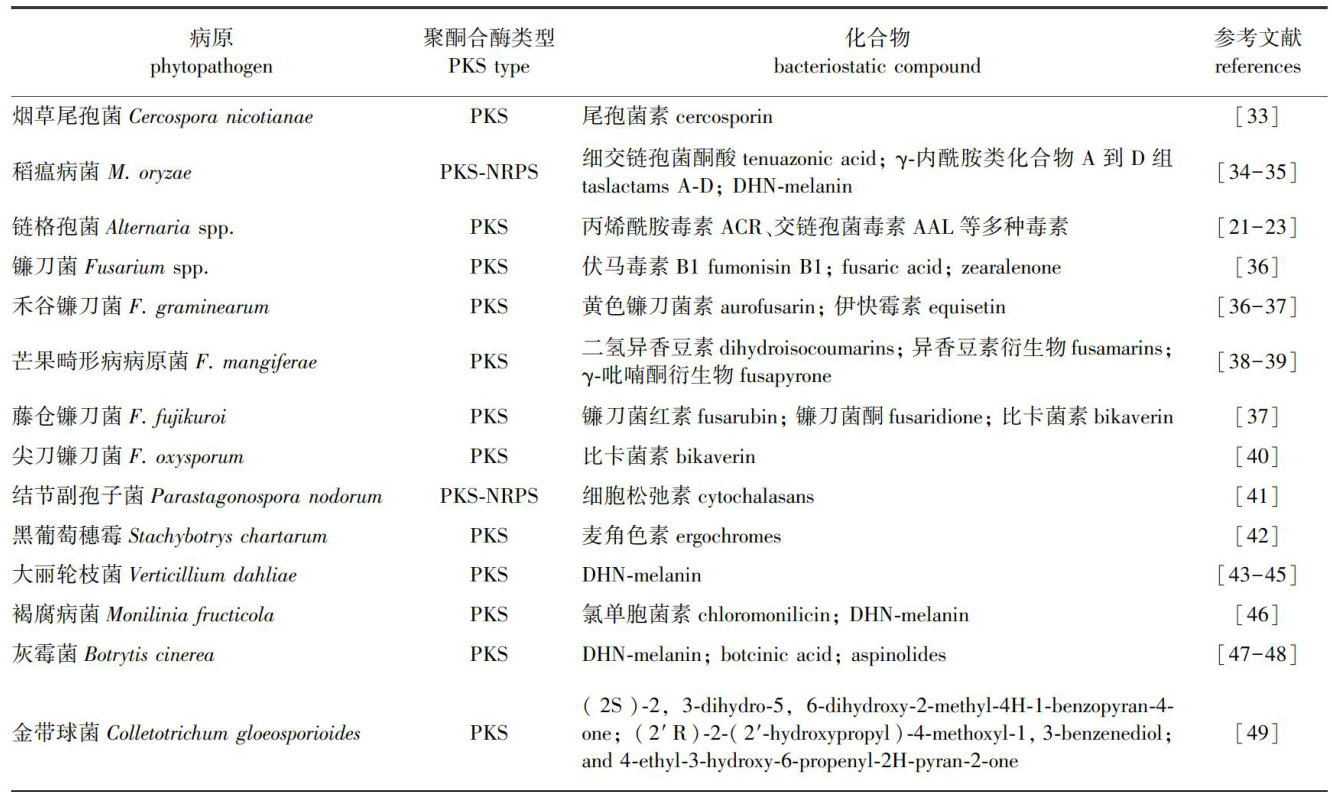
真菌在生命活动中会产生许多分子量低、具有生物活性的物质,被称为次级代谢产物[1],虽然次级代谢产物对其生存并非必要,但在生态位适应、繁殖、耐胁迫、竞争及互作等方面具有重要意义[2]。(剩余21762字)