维持性血液透析患者数字健康素养现状及影响因素

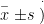
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:R473 文献标志码:A
文章编号:1672-7010(2025)03-0098-08
Abstract: Objective To assess the digital health literacy(DHL) status and influencing factors in maintenance hemodialysis (MHD)patients,providing evidence for developing DHL interventions to improve nutritional status and quality of life.Methods Using convenience sampling,71O MHD patients from four hemodialysis centers across three tertiary hospitals in Shaoyang (November 2O24 to January 2025) were enrolld. Data were collcted through a general demographic questionnaire,a digital health literacy scale,and an MHD patient nutritional literacy assessment.The DHL status and its influencing factors were analyzed. Results A total of 710 MHD patients were included. The median total DHL score was [18.00(12.00,32.00)], with median subscores of[8.00 (4.00,12.00)]for interactive DHL,[6.00 (5.00,14.00)] for critical DHL, and[3.00(3.O0,6.25)]for functional DHL.The mean nutritional literacyscore was 85.69±12.91.Univariate analysis revealed statistically significant differences ( P <0.05)in DHL based on gender,age,education level, monthly income,source of payment,nutrition literacy level,and online health-information-seeking behavior. Conclusion DHL in MHD patients was suboptimal,with key influencing factors including gender,age, education level,monthly income,source of payment,nutrition literacy level,and online health informationseeking behavior.Healthcare providersshould prioritize enhancing patients’digital tol operational skils, guiding their access to and comprehension of health information,thereby improving DHL to optimize nutritional status and quality of life.
Key Words:maintenance hemodialysis;digital health literacy;nutrition literacy;influencing factor
近年来,慢性肾脏病(chronic kidney disease,CKD)的患病率逐渐升高,世界范围内CKD的患病率为 9.1% ,其中终末期肾病(end-stage kidneydisease,ESKD)的患病率为 0.2%. )0.4% ,且正以每年约 9% 的速度持续增长[1]。(剩余6694字)