基于CT平扫的预测模型对肺梗死与胸膜下肺炎的鉴别诊断价值

打开文本图片集
ValueofapredictivemodelofCTnon-enhancedfeatures indiferentialdiagnosisbetweenpulmonaryinfarctionand pneumonia
DONGHaixia,ZHANG Youjun,JIANG Ruisheng,ZHANGWanwei,JIANG Changqin
Department ofMedical Imaging,Weifang Yidu Central Hospital,Weifang 2625oo,China.
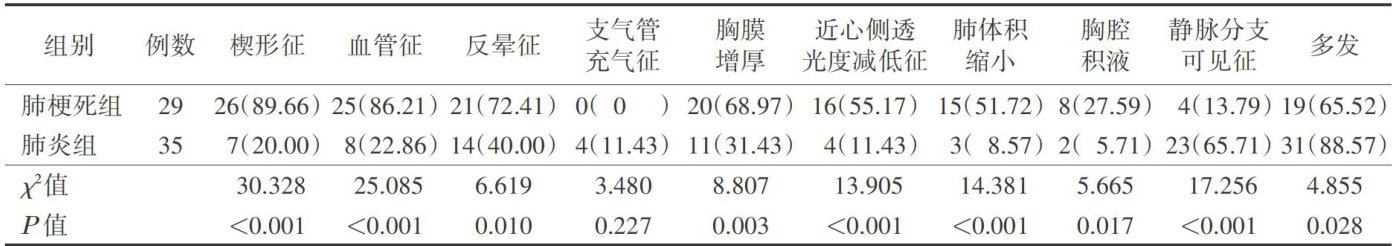
[Abstract]Objective:ToexplorethevalueofapredictivemodelofCTnon-enhancedfeaturesindiferentialdiagnosis betweenpulmonaryinfarctionandpneumonia.Methods:Chest CTimagesof29patientswithpulmonary infarctionand 35patientswithpneumoniawereanalyzedretrospectively.Univariateandmultivariatelogisticregressionanalysiswere performedtoanalyzethefactors,includingthewedgesign,vascularsign,reversedhalosign,pleuralthickening,decreased proximalcardiactransmitance,lungvolumereduction,pleuralefusion,venousbranchsign,andairbronchogramsignAndthe predictivemodelwasestablished.ROCcurvewasusedtoanalyzethediagnosticeficacy.Results:Therewerestatitically significantdiferencesinthewedgesign,vascularsign,reversedhalosign,pleuralthickening,decreasedproximalcardiac transmittance,lung volume reduction,pleural effusion,venous branch sign (all P<0.05 ).The venous branch sign was more commoninpneumonia,theotherfeaturesweremorecommoninpulmonaryinfarction.Multivariatelogisticregresionanalysis showed hat wedgesignwasindependentpredictorof pulmonaryinfarction,whilevenousbranch signwasprotective factorof pneumonia.TheAUCofthecombinedmodelconstructedwithwedgesignandvenousbranchsignreachedO.925,higherthan that of wedge sign and vascular sign separately (both P<0.05 ). Conclusion:The combined model constructed with wedge sign and venous branch sign can accurately diffrentiate pulmonary infarction from pneumonia.
[Keywords] Pulmonary Infarction;Pneumonia;Tomography,X-ray computed;Nomogram
肺血栓栓塞症(pulmonarythromboembolism,PTE)是常见的内科危重症之一,发病率和病死率均较高[1-2]。(剩余7708字)