黄河流域中游生态系统服务价值时空变化特征及驱动因素

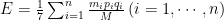
打开文本图片集
关键词:生态系统服务价值;土地利用变化;XGBoOst—SHAP模型;黄河流域中游中图分类号:X171.1 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1671-8151(2025)05-0125-12
Abstract:Objective]Factorssuchasloosesoiltructure,significantterrainundulation,andlowvegetationcoveragecontribute topoorecologicalstabilityintheLoess Plateauregion,makingthemiddlereachesof theYelowRiveratypicalareaofprominentecologicalvulnerabilityinChina.Acuratelyestimatingthedynamicchanges inecosystemservicevalue(ESV)and its influencing factors isofgreatsignificanceforpromoting sustainabledevelopmentin this region.Methods]This studycostructed anESVvaluationmodelthatincludedconstructionland,basedonamodifiedequivalentfactor method.Usingtheland use transfermatrixandXGBoost-SHAPmodel,weexaminedthedynamicevolutionoflanduseandESV,aswellasthefactors influencing ESVinthe studyarea.[Results](1)Landuse typesand transitionsin the middlereachesoftheYelow RiverBasin were primarilycharacterizedbycultivatedLand,grassland,andforest.Thedynamicchanges insinglelandusetypes,particularly cultivated land and construction land,were significant,with rates of -2.95% and 1.90% ,respectively. The comprehensive land use dynamic degree averaged 0.15% ,peaking at 0.32% from 2005 to 2Olo.(2) The total ESV in the middle reaches of the Yellow River Basin gradually decreased,with an overall reduction rate of 21.95% . Areas with low and medium ESV shrank,whiletosewithigherESVexpanded,presentingaspatialdistributionpaterthatdecreasedfromnorthwesttosouth east.(3)Nighttime light intensity was the most significant factor affcting ESV changes,accounting for 23.03% .Average slope,forest proportion,andannualaverage temperaturehad positiveefectsonESV,whereas nightimelight intensity,culti vatedlandproportion,populationdensity,andaverage altitudehadnegativeefects.The influenceofotherfactors wasrelatively minor.[Conclusion]Due torapid economicdevelopmentandthegradualadvancement ofurbanization,theESVinthe middlereachesoftheYellowRiverBasinshowedadecreasing trend.Itisessentialtodeepentheunderstandingof theimpactsof naturalandhumanactivitiesontheecologicalenvironment.Thefindingsofthisstudycanprovidescientificsupportforoptimizingthespatialpaternofecosystemservicesandformulatingecologicalprotectionstrategies inthemiddlereachesoftheYellow River Basin.
Keywords:Ecosystemservices value,Landusechanges,XGBoost-SHAPmodel,MiddlereachesoftheYelowRiverBasin
生态系统服务(ES)是指人类从自然界中获得的直接或间接利益。(剩余20299字)