西葫芦雄性不育理化特性与转录组分析

打开文本图片集
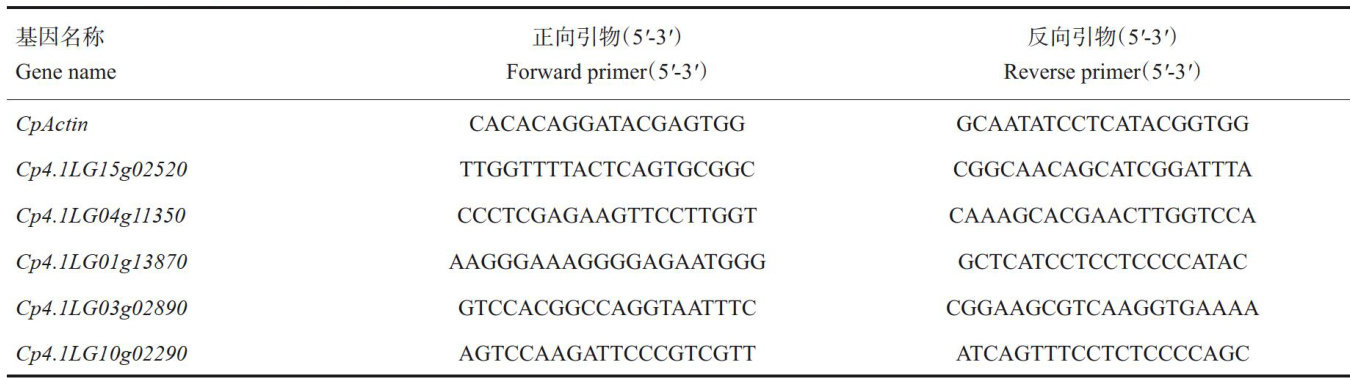
Abstract: Research on male sterility mechanism of Cucurbita pepo L. is of great value for enhancing breeding and hybrids production.Using male sterile (X-MS)and fertile plants (X-MF)of zucchini as experimental materials,this study integrated transcriptome sequencing with analysis of endogenous hormone contents,antioxidant enzyme activities,sucrose/starch content.Results demonstrated that during anther developmental stages-tetrad(T1),early uninucleate (T2),mid-late uninucleate(T3),binucleate(T4),preanthesis(T5),the abscisic acid content,gibberelin content,and auxin content(T1-T3)of X-MS male flower buds lower than X-MF,exhibited reduced performance,an increasing trend in peroxidase activity,and decreasing trend instarchand sucrose content.Transcriptome sequencing identified1947diferentiallyexpressed genes (DEGs)from T1 to T3,comprising 91l up-regulated and 1036 down-regulated genes.GO enrichment analysis revealed catalytic activity and binding as the most anotations in molecular function,while celular and metabolic processes dominated biological process annotations.KEGG analysis showed significant DEGs enrichment in pathways such as plant hormone signal transduction,phenylpropanoid biosynthesis,starch and sucrose metabolism,and amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism.Further analysis of plant hormone signaling,phenylpropanoid biosynthesis,and starch/sucrose metabolism pathways identified candidate genes including one peroxidase-related gene,one sucrose synthase-related gene,and two IAA-related genes related to. These genes may play pivotal roles in pollen development of male-sterile zucchini and provide mechanistic insights for future research on male sterility in zucchini.
Key words: zucchini(Cucurbita pepo L.);male sterility; physiological and biochemical; transcriptome sequencing;differentiallyexpressed genes
西葫芦(CucurbitapepoL.),别名美洲南瓜,来源于美洲,是重要的葫芦科南瓜属蔬菜之一。(剩余19722字)