泛素化调控植物免疫反应研究进展

打开文本图片集
Abstract:Fungal diseases constitute one of the key factors in crop yield reduction,posing a serious threat to global agricultural production and food security.When plants are attcked by pathogenic fungi,their defense mechanisms primarily involve the complex regulation of disease resistance related protein synthesis and posttranslational modifications.In recent years,the role of ubiquitination in regulating plant immune responses has gained significant prominence in plant pathology and molecular biology.Ubiquitination,as acritical posttranslational modification mechanism,participates in pattern recognition receptors (PRRs)-mediated signal transduction pathways.It influences receptor endocytosis,degradation,and recycling,thereby enhancing the plant'sability to recognize pathogens.Furthermore,ubiquitination interactswith plant hormone signaling pathways to colectively regulate disease resistance.As a central component of the ubiquitination process,the diversity and specificity of E3 ubiquitin ligases enable precise immune response modulation in plants.This review mainly introduces the reaction process of the ubiquitin-proteasome system and focuses on the regulatory roleof protein ubiquitination in plant immune responses,as wellas the functional studies of ubiquitin ligases in plants'response to pathogen infection.The aim is to provide new strategies and technical means for a deper understanding of the mechanisms regulating plant resistance and for breeding crop varieties with enhanced resistance. Investigating ubiquitination in the context of plant immune responses is of great significance for advancing this field.
Key words: plant immunity;ubiquitination modification;E3 ubiquitin ligases
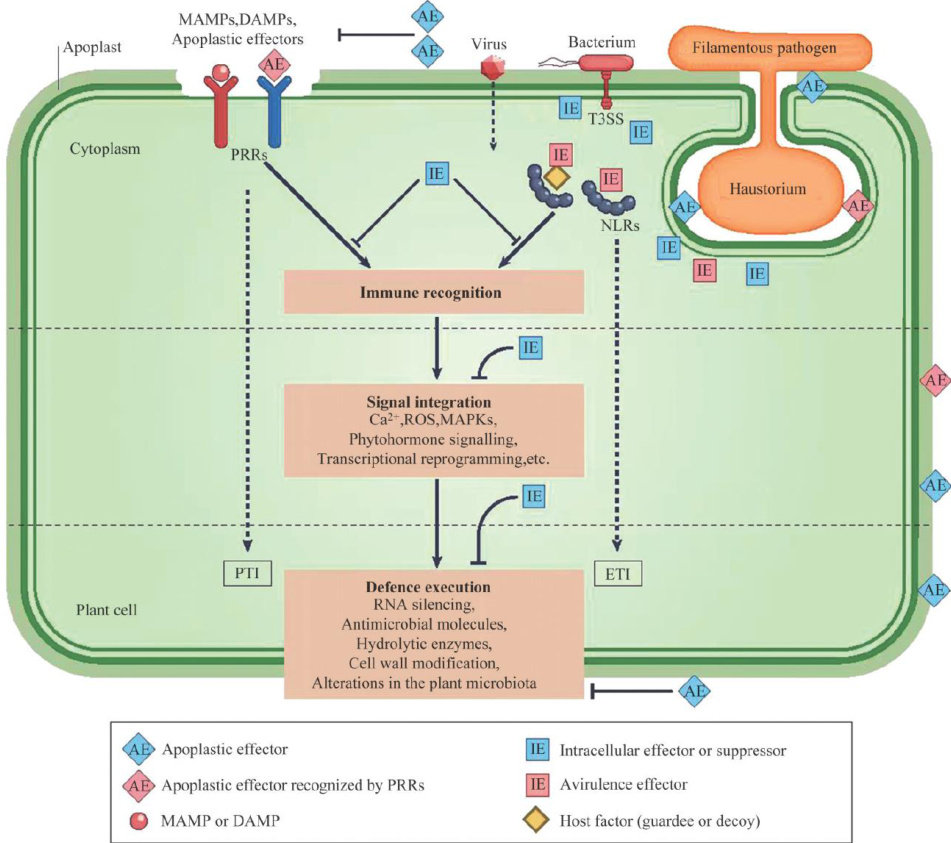
植物在自然界中面临各类病原菌的挑战时,为了确保其正常的生长发育,植物体内会经历一系列的代谢变化以保持并调整细胞的正常生理机能。(剩余41048字)