玉米卷叶突变体swI5的基因定位及功能分析

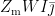
打开文本图片集
Abstract: Drought represents a significant constraint affecting maize growth and development. Identifying drought-resistant genes is vital for genetic improvement of drought resistance in maize.In this study,the leaf roling mutant swl5 (sensitive to water loss 5)was identified from the EMS-mutagenized mutant library of the inbred line RP125.The swl5 mutant exhibited distinct leaf wilting and rolling phenotype under field drought stress.Map-based cloning localized the genetic locus to a physical region of 280kb on chromosome 5, containing nine predicted coding genes.In this interval,a C to T mutation occurred at the 748th nucleotide of the GRMZM2G002260 gene,resulting in a premature stop codon. GRMZM2G002260 corresponds to the previously reported ZmWI5,encoding an endo-1,4-xylanaseof the GH10.To further validate gene function,the wi5 mutant allele of ZmWI5 was obtained. The F1 plants derived from the cross of swl5 and wi5 mutant displayed leaf wilting and rolling phenotypes to both parental mutants. Under drought stress,the swl5 mutant showed significantly reduced photosynthetic rate,stomatal conductance,and transpiration rate compared to the wild type RP125, while displaying elevated leaf temperature and increased accumulation of H2O2 and O2- .Expression of genes involved incellulose synthesis(CESA5)and xylan synthesis(DUF579,GT47,IRX9,IRX9H-1,IRX9H-2, GUX1,TBL33)was significantly down-regulated in swl5 under both well-watered and drought stress.In summary,swl5 is anew allelic mutation of the ZmWI5 gene.The swl5 mutant exhibits a drought sensitive phenotype,and the expresson of genes related to xylan synthesis is significantly reduced in the mutant.
Key words:maize;rolled-leaf mutant;gene mapping;drought
玉米(ZeamaysL.)是我国重要的粮食作物,其种植面积和总产量已超过水稻成为我国第一大粮食作物。(剩余15188字)