小麦穗部性状近等基因系的创制及穗粒数候选基因分析

打开文本图片集
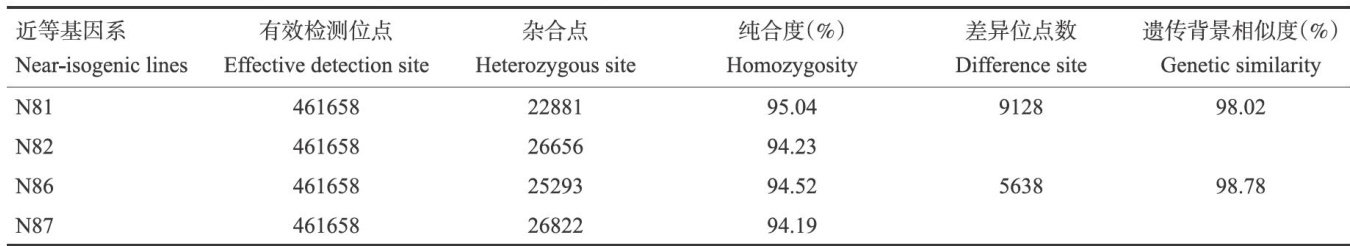
Abstract:To develop novel genetic materials with breeding potential and identify genetic intervals regulating grain number per spike in wheat,weconducted acomprehensive study using near-isogenic lines (NILs)through crossing the octoploid Thinopyrum ponticum derived wheat cultivars Hengguan 35 and Kenong 199.Seven yield-related traits,including plant height,effctive tiller number,spike length,spikelet number per spike,grain number per spike,grain yield per plant and thousand grain weight,were systematically evaluated. Genome-wide scanning was performed using the 66oK SNP array to identify polymorphic loci and conserved physical intervals between two pairs of NILs.Candidate genes were predicted through integratedanalysis of gene anotationand expression profiles within thecandidate regions.The results indicated that NIL pairs N81/N82and N86/N87 exhibited significant differences in spike-related traits while maintaining genetic similarities of 98.02% and 98.78% ,respectively. SNP polymorphism analysis identified three conserved genomic regions associated with spike architecture,662-669 Mb onchromosome1B,19-25Mb on chromosome 3B,and 541-548 Mb on chromosome 5B.Through integration of QTL mapping data,gene functional annotation,expression analysis, and orthologous gene comparison,we identified three putative candidate genes regulating grain number per spike:TraesCS1B02G443200,encoding malate dehydrogenase on chromosome 1B,TraesCS3B02G042400, encoding an AP2/ERF transcription factor on chromosome 3B,and TraesCS5B02G366500,encodinga C2H2- type zinc finger protein on chromosome 5B.These findings provide a theoretical reference for identifying genes regulating grain number per spike in wheat.
Key words:wheat;66oK SNP array;near-isogenic lines;spike related traits;candidate genes
小麦(TriticumaestivumL.)是世界上重要的粮食作物之一,维持其稳产、增产对确保粮食生产安全至关重要[1-2]。(剩余16545字)