诃子果实性状变异及优树选择

打开文本图片集
Abstract:To comprehensively explore the germplasm resourcesof Terminalia chebula Retz.,this study selected240 candidate individual plants from theNujiang River Basin for analysis.Nineteen fruit traits were assessed,and variation and correlation analyses were performed.Superior individual plants were identified through principal component analysis(PCA),the afiliation function method,anda multidimensional coordinate synthesis method.Theresults demonstrated substantial variation inthe fruit traitsofT.chebula,with coeffcientsof variationranging fromO.03to0.78andanaverageof 0.21.Gallicacidcontent exhibited the highest variability,folowedbypulpweight,total phenols,fruit weight,and kernel weight.Incontrast,traits such as the fruitshape index,water extract,edible rate,and moisturecontent showed relative limited variation. Theediblerate displayedan extremely significant positive correlation with soluble solids and total acid,as well as significant positive correlations with water extract,total phenols,and galic acid content.These findings highlight theediblerateasa critical indicator for the selectionof superiorT.chebula individuals.Moreover, extremelysignificantpositive correlation wereobservedamong total sugar,totalacid,total phenols,and soluble solids.PCA of the19 traits yielded five principal components,collectively accounting for 74.444% of the cumulative variance.Nineexceptional elite plants were identified,with the following serial numbers:BB01, BB13,JZS22,MC18,MC20,MCC12,MK08,MK12,andSJK08.These resultsoffera scientific foundation for the selectionand development of improved varieties of T.chebula,holding significant practical value for future cultivation and resource utilization.
Keywords:Terminalia chebulaRetz.;fruit;trait variation;plus treeselection
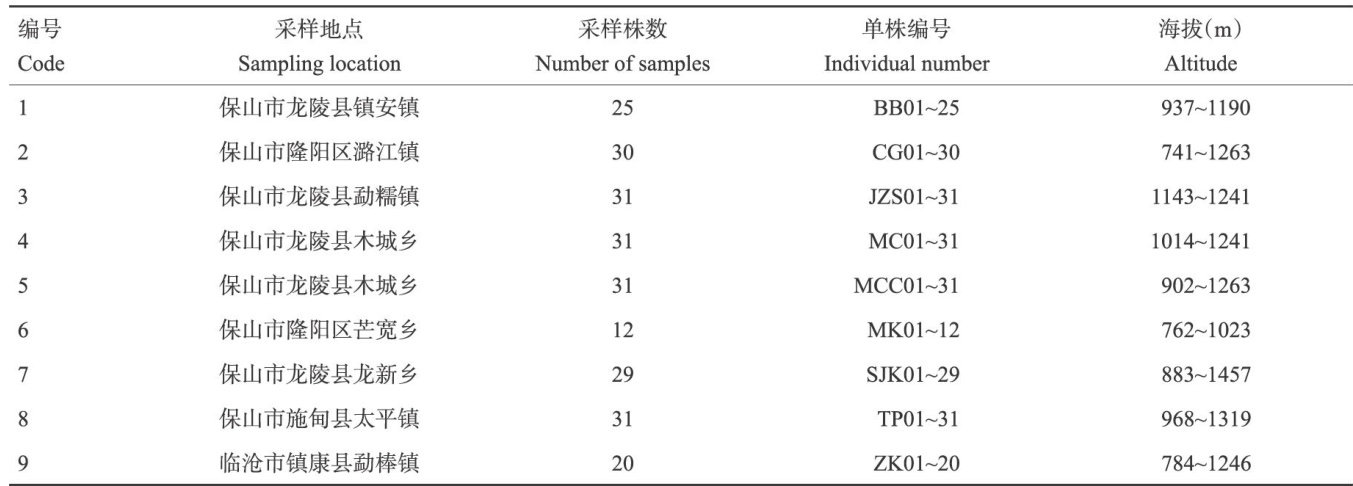
诃子(TerminaliachebulaRetz.),又名诃黎勒、诃得果,为使君子科(Combretaceae)揽仁树属(TerminaliaL.)落叶乔木,分布于南亚和东南亚国家,在中国天然分布集中于怒江流域海拔 1100m 以下的河谷地区[1-4]。(剩余17170字)