769份绿豆种质资源萌发期耐盐性鉴定

打开文本图片集
Abstract:The salt tolerance of mung bean at germination stage is an important index for its utilization in saline-alkali soil.Identification of germplasm with high salt toleranceat germination stage can improve the utilizationrate ofsalinization land.In the present study,based the pre-experiment,we selected 1.2% NaCl as the best solution for identification of 769 mung bean accessions at their germination stage,by measuring germination rate(GR),germination potential(GP),germination index(GI),relative salt damage rate and other indexes through hydroponic experiments.The results showed that the average germination rate of mung bean germplasm under 1.2% NaCl salt stress was 52.9% .Among different regions,the average germination rate of resouces from East Asia is the highest( 66.5% ),while it is the highest from Northeast China ( 57.4% ).The degree of variation in germination potential is the highest among allindexes under salt stress (CV: 58.0% ),particularly the germplasm from the North China region,its coefficient of variation reached 63.2% .Among germplasm with different coat colors,the salt tolerance of brown-grained germplasm was notablyweaker than that of other colored seeds,while the mung bean germplasm with luster seed coat had significantly greater tolerance than the dull-surfacedresources.Theanalysis revealeda significant correlation between the 100-seed weight and their salt tolerance,with germplasm weighing less than 3g showing a marked decrease in salt tolerance.This study offr data support for the selection ofsalt-tolerant germplasm
andvarietybreedinginmungbean
Key words: mung bean; germplasm resources; germination stage;salt tolerance;phenotypic variation
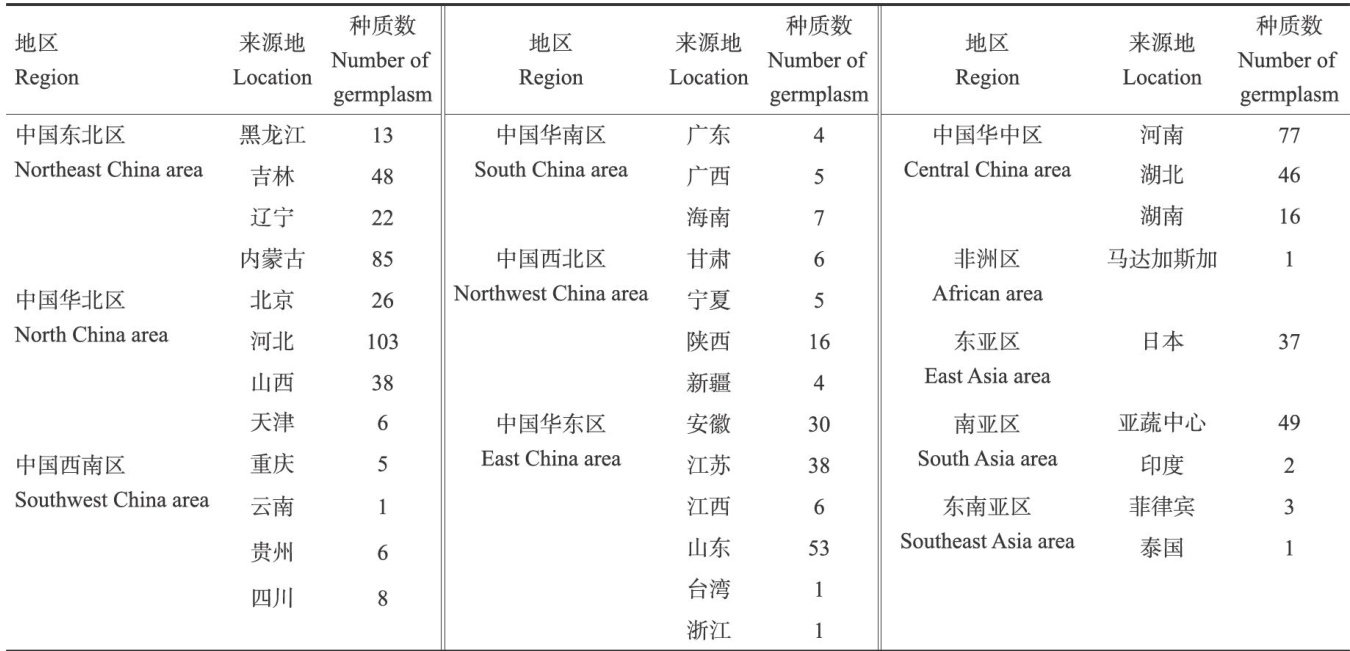
土壤盐渍化是指可溶性盐离子在土壤表层( 0~ 30cm )积聚,导致土壤呈现不良特性、质量下降,从而影响植物生长和农业生产[1-2]。(剩余13341字)