寻找腹主动脉瘤的潜在治疗靶点:基于汇总数据的孟德尔随机化及基因表达综合数据库的研究

打开文本图片集
Identifying potential therapeutic targets for abdominal aortic aneurysm:a summary data-based Mendelian randomizationand geneexpressionomnibusstudy
Guo Yujie DepartmentofVascular,hanxiProvincialPeople'sHospital,ShanxiMedical University,TaiyuanO3o2,Cina
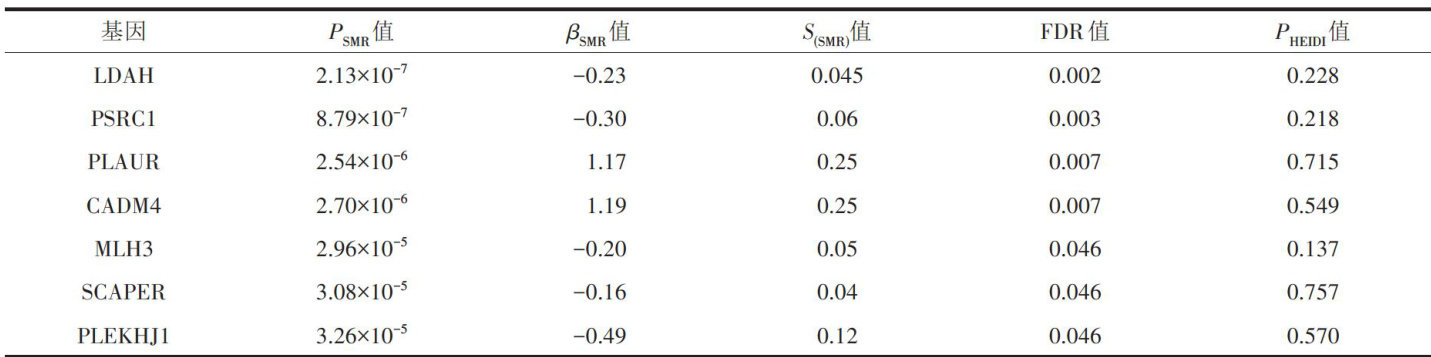
【Abstract】 ObjectiveTo investigate potential pathogenic genetic loci contributing to abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA)development through summary-data-based Mendelianrandomization (SMR) research,thereby providing novel insights forthe treatment of this condition.MethodsWe employed the SMR method to pinpoint genetic loci closely linked to AAAandsubsequentlyvalidated thesegenes by comparing themwithdiferentially expressed genes obtained from the gene expression omnibus (GEO)database in order to identify core genes. Subsequently,we conducted a SMR analysis on theGWAS datarelated to core gene loci and AAA to further substantiatethe efectiveness of the core genes.Finally,weperformed GSEAto gain deeper insights into their pathophysiological mechanisms.ResultsThrough the SMR test,we have identified 7genes closely associated with AAA.Upon integrating these genes with diferentially expressed genes from the GEO database,we pinpointed the core gene:PLAUR.SMR testing further validated itsassociation with AAAand itsrole in promoting disease development [OR(95%C1)=1.45(1.01, 2.07), P=0.043] .OurGSEA hasled usto hypothesize that this functionmaybe mediated through the lysosomal pathway.ConclusionThis SMR studysuggests apotential causal asociation betweenPLAURandAAA.
【Key words】 Aortic aneurysm,abdominal;Mendelian randomization; Summary-data-based ;UrokinasereceptorDOI:10.19522/j.cnki.1671-5098.2025.09.005
腹主动脉瘤(abdominalaorticaneurysm,AAA)的定义是腹主动脉的局限性扩张,并且扩张程度超过正常血管直径的 50% 。(剩余17103字)