流动电极电容去离子去除铜离子的性能与系统污染研究

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:P747 文献标识码:A DOI:10.7535/hbkd. 2025yx06012
Abstract:In order to address the issue of system contamination caused by the treatment of copper ions ( Cu2+ )wastewater usingelectrochemicaltechnology,whichleads topoorsystem stability,thispaper focusedonthepolutioncharacteristicsof the system during the removal of Cu2+ byflow electrode capacitive deionization(FCDI),and explored the influence mechanism of key parameters such as applied voltage,inlet Cu2+ concentration,flow electrode velocity,and inlet water quality on the Cu2+ removal performance of the system.The results show that under the conditions of an applied voltage of 0.8V ,an influent Cu2+ concentration of 50mg/L ,and a flowing electrode flow rate of 1.2mL/min ,the Cu2+ removal rate reaches 56.22% ,the charge efficiency is 90% ,and the copper removal rate is 0. 03μmol/(cm2⋅min) .At the same time,the continuous operationstabilityoftheflow electrodesystemunderdiferentcyling modesisinvestigated,andthepolution characteristicsof theionexchange membraneandactivatedcarbonelectrodeareanalyzed.Theresultsindicatethattheflow electrodeexhibitssignificant advantages incopper ionremovalunderthesinglecycle(SC)mode,and themembraneand electrodeexhibitthelowestlevelofpollution.ThisstudyprovidesimportantreferencefortheappicationofFCDItechnologyin heavy metal removal.
KeyWords:otherdisciplinesofenvironmentalengineering;copper wastewater;FCDI;copperionremoval;electrode fouling; membrane fouling
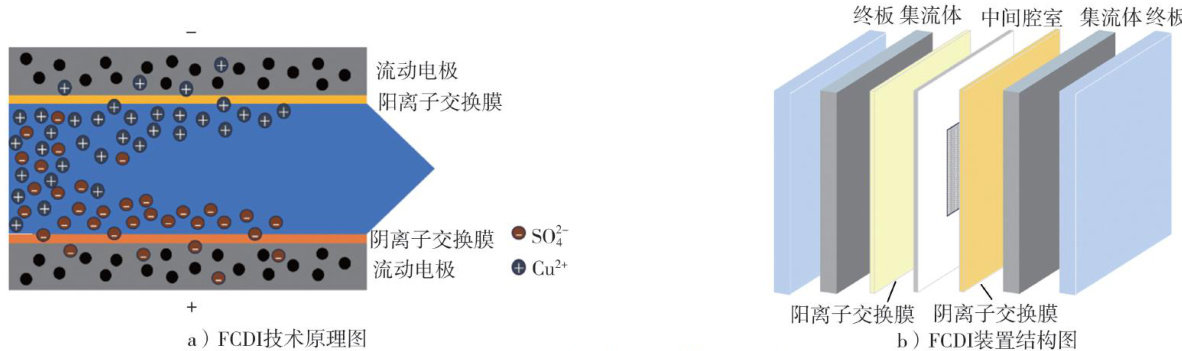
随着工业化进程的加快,水体中重金属离子污染问题日益严重。(剩余12767字)