1997—2021年川渝地区区县尺度碳排放时空格局特征分析

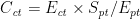
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:X321 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1673-5072(2025)04-0358-09
Abstract:The -Chongqing region,as an important leading area for development in the western part ,is required to realizesynergistic development green low-carbon initiatives with regional coordination.Scientifically exploring the regional differences fine-scale carbon emissions in Chongqing is great importance for carbon emission reduction.Utilizing a panel data model, based on the provincial carbon emissions nightime lightdata from 1997 to 2O21,county-level carbon emission data were estimated.Meanwhile,employing ArcGIS stware,the spatiotemporal variation trends carbon emissions across 21 districts counties in the -Chongqing region were investigate. The results indicated that the constructed estimation model demonstrates a high level accuracy ( R2=0.979 ,with an average absolute percentage error(MAPE) 5.716% ).The carbon emissions at the county level in the -Chongqing region exhibit significantregional differences in both time space,along with distinct spatial agglomeration characteristics.The -Chongqing urban agglomeration,as a high-carbon emission area,the carbon emissions there show a trend increasing followed by a decrease around 2O12.In contrast,the carbon emissions in the western counties are relatively low but continue to grow.Overall,the carbon imbalance at the county level within the entire Chongqing region or either the two provinces is improving year by year.The study findings suggest that fine-grained data can better reflect localized heterogeneity withina large area.
Keywords:carbon emission;nighttime lighting;-Chongqing region;spatio-temporal variation;spatial autocorrelation
自改革开放以来,中国经济快速发展,工业化和城市化进程迅猛推进[1],导致能源需求和消耗急剧增加,使得二氧化碳排放量大幅提高[2]。(剩余13245字)