番茄SDof14基因参与调控果实成熟进程

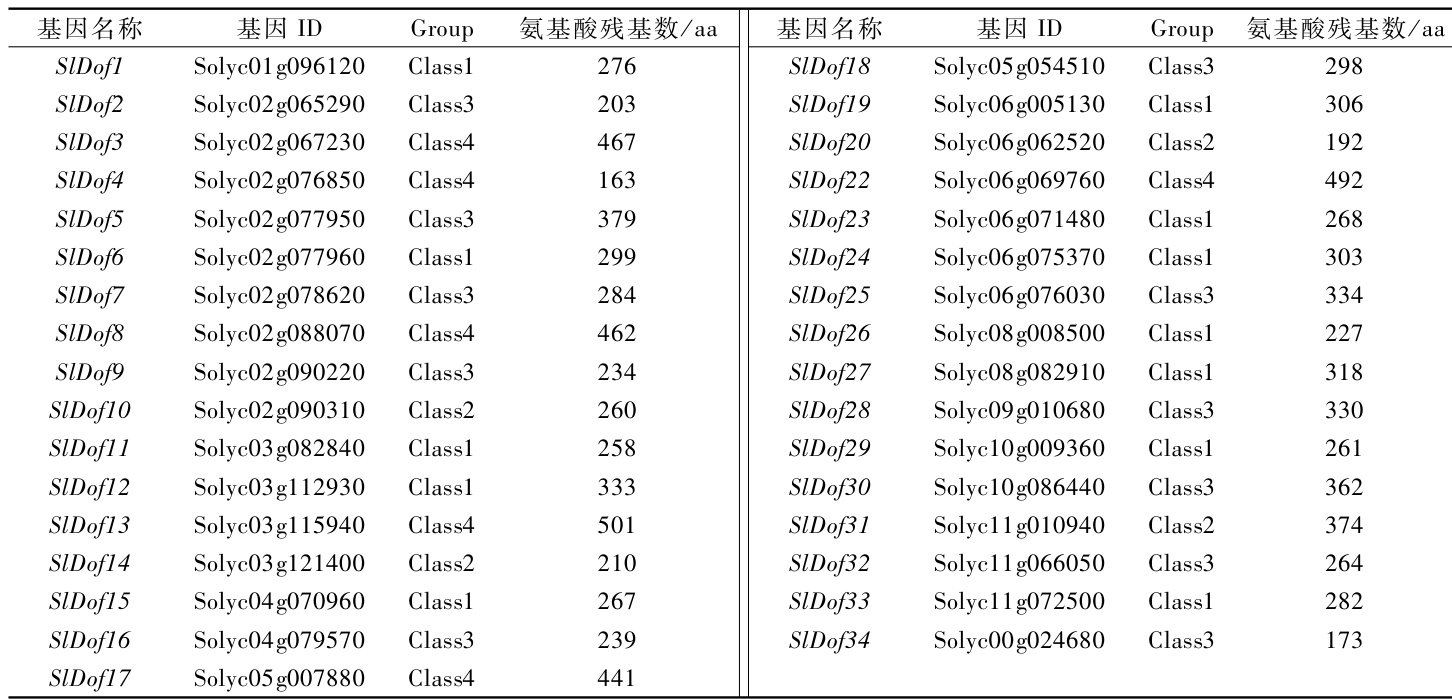
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:Q37 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1673-5072(2025)03-0238-10
Abstract:Tomato(Solanum lycopersicum) is a model plant for studying the ripening of fleshy fruits, whose ripening process is regulated by both ethylene signaling and related transcription factors.Based on the tomato genome database and transcriptome database,Dof genes related to tomato fruit ripening were screened,and their expression at different temperaturesand hormone levels wereanalyzed to identify the key Dof genes for fruit ripening,as well as their relationship with the ethylene signaling pathway.As a result,three Dof genes,including SlDof3,SlDofl0,and SlDofl4,are identified with relation to tomato fruit ripening by detecting gene expression levels under low-temperature treatment,exogenous ethylene,and inhibitor treatment.And SlDofl4 may be asociated with the ethylene signaling pathway.The further analysis shows that the expresson level of SlDofl4 gene in tomatoes gradually increases with fruit ripening and aging,while it is strongly inhibited by low temperature treatment;exogenous ethylene has a strong promoting effect on the expression of SlDofl4,but 1-MCP shows a strong inhibitory effect;the expression level of SlDofl4 in the fruits of Rin is lower than that of wild-type tomatoes in the early stage of ripening(MG and Br stages),but it gradually increases and then becomes higher than that of wild-type tomatoes.In addition,there are MYC and MYB specific recognition elements in the upstream region of the SlDofl4 promoter,which are the important genetic factors in the ethylene synthesis pathway,indicating that SlDofl4 may work together with ethylene signaling to regulate the early process of tomato fruit ripening.
Keywords: tomato ; fruit ripening; SlDof gene;low temperature ;ethylene
果实成熟过程中,其色泽、风味、香气和口感等品质的变化与一系列的生理生化反应有关,其中乙烯和脱落酸(ABA)在促进果实成熟过程中发挥着至关重要的作用[1-2]。(剩余14640字)