小鼠感染猪致病性大肠杆菌模型的构建与病理研究

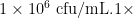
打开文本图片集
Abstract:PorcinepathogenicEscherichiacoli,isanimportantpathogenthatcausesintestinaldisease,septicaemiaand urinary tract infections.Inordertoexploretheinjury mechanisminducedbypathogenic Escherichia coli,this experiment randomly divides 50 8-to 9-week-old Babl/c female mice into 10 groups,with 5 mice in each group.Four model groups areintraperitoneallyinjected with 300μL E.coli at concentrations of 1×106 cfu/mL, 1×107 cfu/mL, 1×108cfu/mL 1×109 (204号 cfu/mLrespectively,while thecontrol groupmiceare intraperitoneallinjected withanequal volumeofsterilizedPBS. After72hoursofobservation,thehistopathological changesareobservedand thecelular inflammatory factors interleukin-2(IL-2)and interleukin-6(IL-6)aredetected.Theprokaryoticexpressionvectorexpressinggreenfluorescent protein(GFP) is transformed into pathogenic E coliEC2316 by electroporation transformation method,and the strain EC2316-GFPexpressng green fluorescence is obtained.The results show that the median lethal doseof strain EC2316 is 2×107 cfu/mL.The bacterial colonization in organs increases with rising bacterial concentration,and IL2 and IL-6 increased significantly.The introductionof GFPdid not alters the growth characteristicsof strain EC2316.In summary, the pathological changes and inflammatory responses observed in mice infected with porcine pathogenic E⋅ coliclosely resemble those documented in naturally occurring cases.A mouse model of porcine pathogenic E .coli infection is successfullyestablished,whichprovidestheoreticalandpractical foundation forfurtherresearch intothedamage mechanisms caused byE.coli.
Keywords:Porcine pathogenic Escherichia coli; GFP;LD50;mouse model
猪致病性大肠杆菌病(PorcinepathogenicEscherichiacoli),是危害猪养殖业的一大挑战,研究显示,该疾病在引发猪只死亡原因中占有显著比例,尤其是对仔猪群体构成了严重威胁[1,2]。(剩余9640字)