脊髓损伤型胸腰椎骨折病人术后早期发生低氧血症预测模型的建立

打开文本图片集
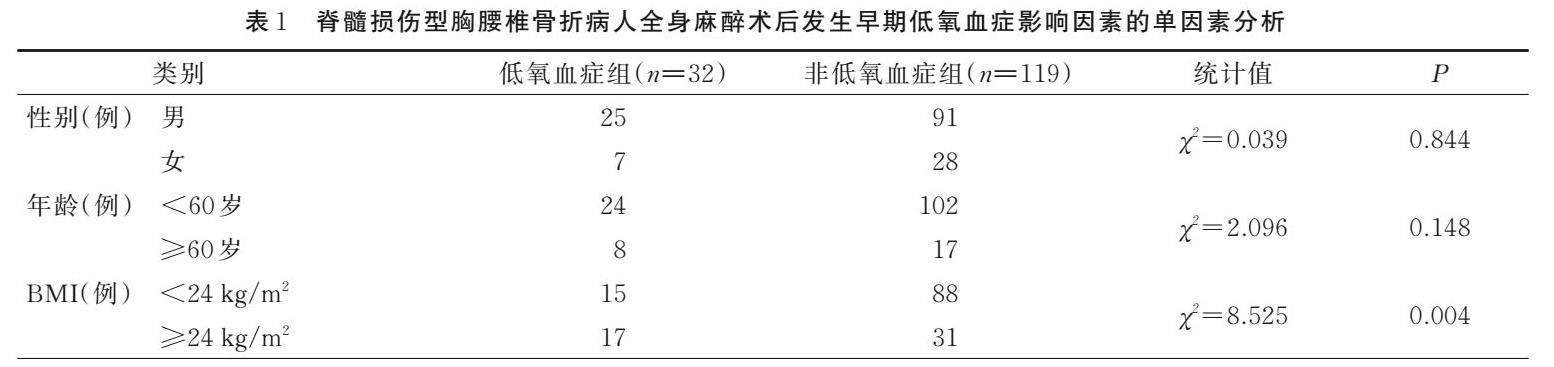
Abstract Objective:To construct a early warning model to investigate the risk factors of early postoperative hypoxemia in patients with spinal cord injury⁃type thoracolumbar fractures.Methods:A total of 151 patients with thoracolumbar fractures admitted to our hospital from May 2017 to March 2021 were selected as the research subjects.The clinical data of the patients were collected.The univariate analysis and Logistic regression were used to analyze early postoperative hypoxemia risk factors in patients with spinal cord injury⁃type thoracolumbar fractures.A nomogram prediction model was established accordingly.Results:Hypoxemia occurred in 32 patients 1 hour after the operation,and the incidence rate was 21.19%.Logistic regression analysis showed that higher body mass index (BMI),hypertension,diabetes,higher American Spinal Injury Association(ASIA) classification,and postoperative hypothermia were independent risk factors for early postoperative hypoxemia in patients with spinal cord injury⁃type thoracolumbar fractures(P<0.05).A nomogram risk model for predicting early postoperative hypoxemia in patients with spinal cord injury⁃type thoracolumbar fractures was established.It has been verified to have good predictive ability.The concordance index(C⁃index) was 0.806,the calibration curve was close to the ideal curve,and the lower area of the receiver operating curve(ROC) was 0.814,95%CI(0.772,0.854),within the range of 8% to 82%.The nomogram predicted a higher net benefit value.Conclusions:Higher BMI,hypertension,diabetes,higher ASIA classification,and postoperative hypothermia are risk factors of early postoperative hypoxemia in patients with spinal cord injury⁃type thoracolumbar fractures.The constructed Nomogram model could effectively predict the risk of incident of postoperative early hypoxemia,which has a certain clinical value.
Keywords spinal cord injury; thoracolumbar fractures; hypoxemia; risk factors; Nomogram
摘要 目的:探讨脊髓损伤型胸腰椎骨折病人术后早期发生低氧血症的危险因素,构建护理预警模型。(剩余10128字)