基于双因子分层约束的深度非负矩阵分解用于高光谱解混

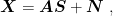
打开文本图片集
关键词:高光谱解混;深度非负矩阵分解;端元判别;正交约束;分层稀疏正则化 中图分类号:TP751文献标识码:Adoi:10.37188/CJLCD.2025-0122 CSTR:32172.14.CJLCD.2025-0122
Deep nonnegative matrix factorization with dual-factor hierarchical constraints for hyperspectral unmixing
QU Kewen*,LUO Xiaojuan,BAO Wenxing
(School of Computer Science and Engineering,North Minzu University, Yinchuan 75OO21,China)
Abstract: Hyperspectral unmixing (HU) is a key technology for addressing mixed pixels and characterizing land cover components. Although deep non-negative matrix factorization (DNMF) has shown excellent performance in HU,existing methods mostly focus on abundance modeling and neglect the multi-level feature extraction of endmembers,as well as their insuficient nonlinear representation capabilities,which limit the unmixing accuracy. To address these issues,this paper proposes a deep NMF framework for endmember hierarchical analysis,introducing inter-layer orthogonality constraints for endmember subspaces and dynamic sparse regularization for abundance refinement. Firstly,multi-level endmember decomposition is employed to enhance the nonlinear spectral feature representation. Secondly,a minimum distance guided subspace orthogonality mechanism is designed to improve the separability of endmembers,and it is coordinated with a dynamic weighted sparsity strategy to enhance the spatial consistency of abundance estimation.Finally,a two-stage hierarchical optimization algorithm is constructed,with pre-training for coarse initialization and cros-layer backpropagation for fine-tuning as the core. Experiments were conducted on two synthetic datasets and four real datasets. The results show that the SAD of the proposed method ranges from 0.004 2 to O.078 2 and the RMSE ranges from 0.014 O to 0.092 5 under different signal-to-noise ratios,outperforming the comparison methods by 1.42% to 5.64% and 1.87% to 6. 48% respectively,verifying its accuracy and robustness.
Key words: hyperspectral unmixing; deep nonnegative matrix factorization; endmember discrimination; orthogonality constraints;hierarchical sparsity regularization
1引言
随着高光谱成像技术的迅速发展,高光谱传感器能够捕获窄且连续波段的地物光谱信息,这不仅强化了对地面的观测能力,还拓展了高光谱遥感图像(HSI在地质勘测、环境监测以及国防建设等领域的应用潜力[]。(剩余24098字)