某三甲医院碳青霉烯耐药肠杆菌目细菌临床分布、流行病学与耐药性分析

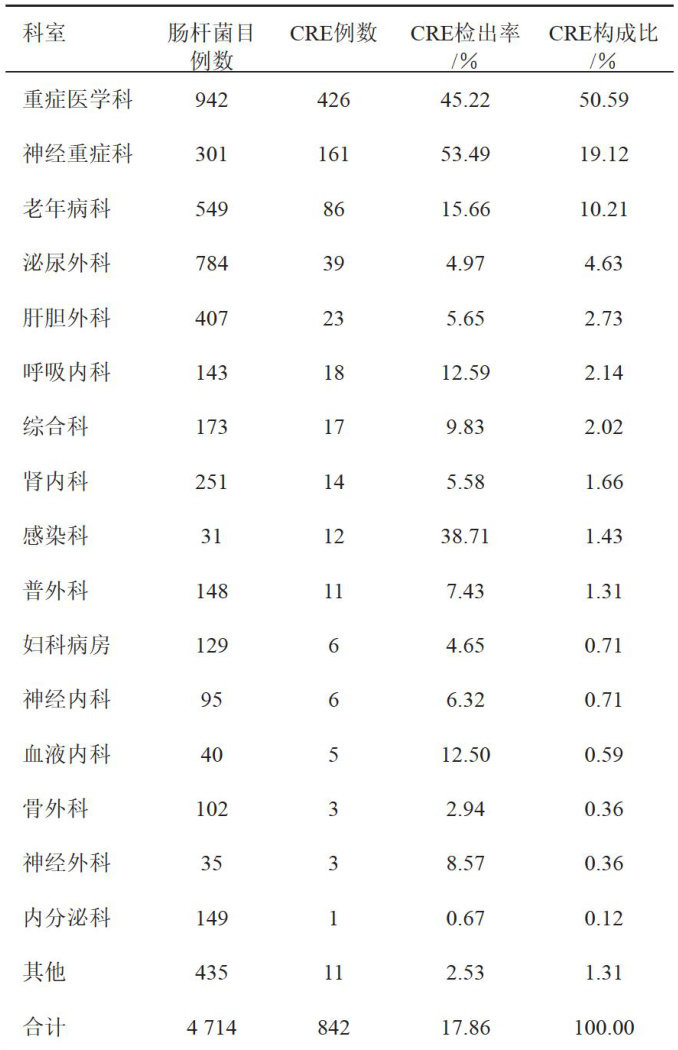
打开文本图片集
关键词:肠杆菌目细菌;CRE肺炎克雷伯菌;临床分布;流行病学;耐药性;抗菌药物中图分类号: R978.1+1 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1001-8751(2025)04-0269-08
Clinical Distribution, Epidemiology and Drug Resistance of Carbapenem Resistant Enterobacteriaceae Bacteria ina Tertiary Care Hospital
Zheng Yuan-ming,LiPei-xuan,Zhou Jie (Dalian Friendship Hospital,Dalian 116001)
Abstract: ObjectiveTo analyze the clinical distribution,epidemiological characteristics and drug resistance ofCarbapenemresistantEnterobacteriaceae(CRE)inour hospital in the last7years,and to provideatheoretical basis for clinical treatmentofCRE infection.MethodsInourhospital,4714 strains of allbacili from 2018 to2024 were examined.Whonet 5.6and SPSS26.0 were used to assessthe clinical distributionand drug resistance,and Excel was used to sort the data inorder to examinethe epidemiological features.ResultsAtotal of 842 CRE strains were detected with a positive rate of 17.86% ,CREwasmainly distributed intheDepartment of Critical Care Medicine (426 strains, 50.59% ),and the detection rate of sputum specimens was the highest (432 strains, 51.31% ), with an increasing trend year by year. Klebsiella pneumoniae was the most common bacteria (656 strains, 77.91% ).Theinfectionof CRE was mainly in elderly male patients,488 cases were detected in patients over 80 years old,and the detection rate was the highest in winter (21.58%) . The drug resistance rate of CRE was generally high. While Enterobacter aerogenes had the lowest rate of resistance to Amikacin (5.9%) ,Klebsiella pneumoniae is completely resistant to both first and second generation cephalosporins as wellas Ampicillin Sulbactam. In over 80% of cases, the MIC of CRE to imipenem and Meropenem was ⩾8mg/L .ConclusionElderlymale patientswith respiratory tract infectionsmade upthe bulk ofCRE patients inourhospital inrecent years.Thenumberofpatients with winter infections is high,and the detectionrateofCRE is rising annually.Monitoringthe drugresistanceofCREand analyzing the epidemiological characteristics of CRE are helpful for the clinical treatment of CRE infection and corresponding prevention and controlmeasures.
Key words: Enterobacteriaceae;CRE Klebsiella pneumoniae;vlinical distribution;epidemiological;drug resistance; antibiotics
随着碳青霉烯类抗生素使用量和强度的增加,碳青霉烯耐药肠杆菌目细菌(Carbapenem-resistantEnterobacterales,CRE)检出率逐年上升,CRE的出现给临床抗感染治疗带来巨大挑战I。(剩余7446字)