脑卒中患者膝关节软骨力学特性分析

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:0382 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1000-4939(2025)04-0940-10
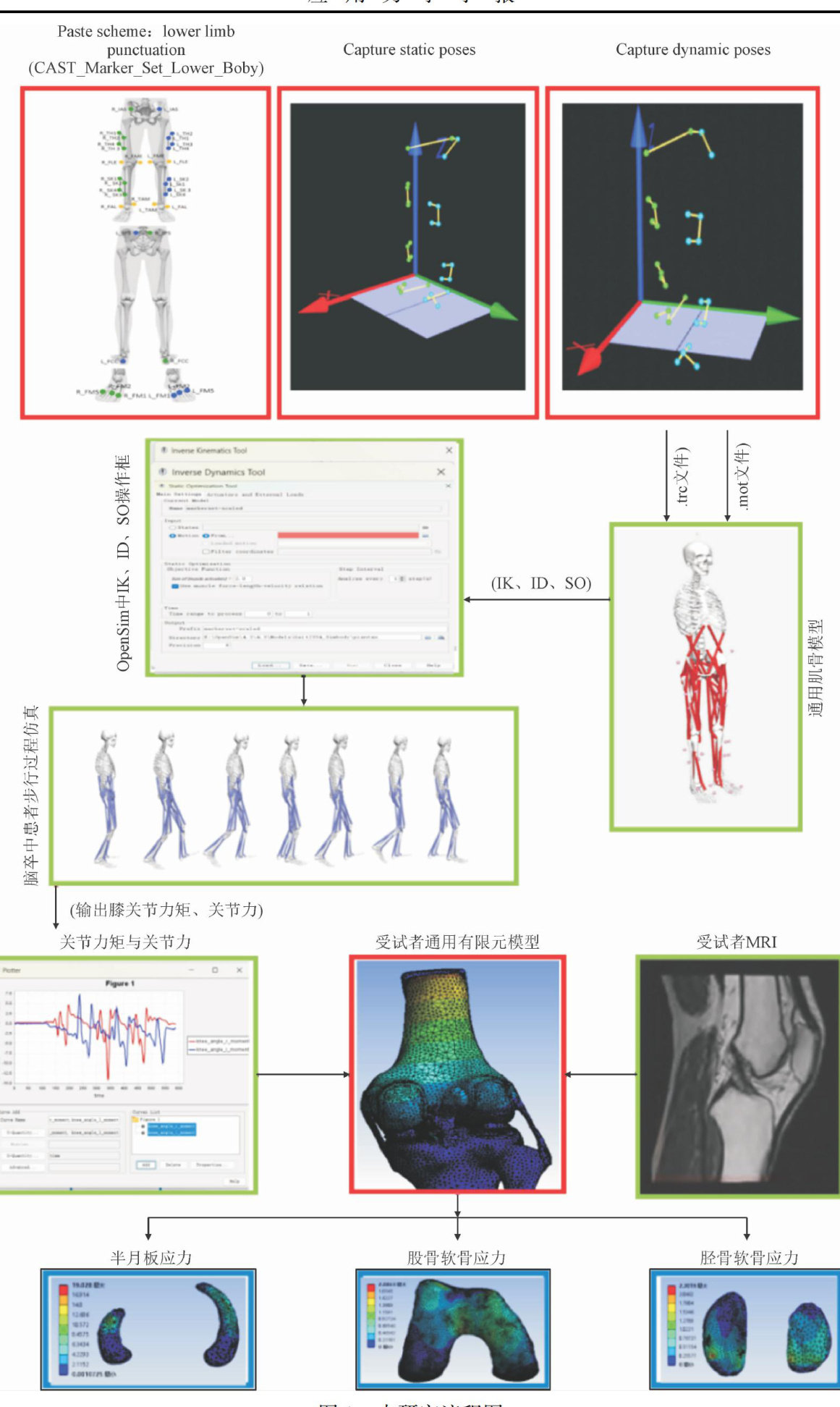
Abstract:This paper makes a comparative analysis of mechanical properties of the cartilage tissues (meniscus,femoral cartilage and tibial cartilage)of knee joints of the healthy side of stroke patientsand the corresponding side of the knee joints of the healthy population.A complete finite element model of the knee joint was established based on MRI and CT; kinematic and kinetic data of walking in stroke patients and healthy people were synchronously collected by an 8-shot Qualisys motion capture system and a Kistler 3 D force platform. Knee joint moments and joint reaction forces were computed by a musculoskeletal model in OpenSim,and the joint moments and reaction forces were used as inputs to the finite element model. The stresses on the knee cartilage tissues (meniscus,femoral cartilage and tibial cartilage)of the two groups were calculated by the finite element analysis software,and the diferences were compared by the independent samples t-test. The peak equivalent force,maximum principal stress,and maximum shear stress of the cartilage tissues (meniscus,femoral cartilage and tibial cartilage) of knee joints on the healthy side of the stroke patients were significantly different from those on the corresponding side of the healthy population (all P values less than O.O1). The FE model can calculate the mechanical properties of knee cartilage tissues in gait analysis of stroke patients,providing a new way to obtain biomechanical data from stroke patients and an effctive way to help prevent cartilage damage in stroke patients. The“healthy” limb of a stroke patient is no longer considered to be truly healthy and should be considered in conjunction with the affected limb in the development of a rehabilitation program.
Key words :stroke; finite element model; meniscus; femoral cartilage ;tibial cartilage
大约 70% 的脑卒中患者会出现偏瘫,其中 40% ~60% 膝关节出现过度伸展[1]。(剩余13399字)