氯化钙改性纳滤膜有效去除饮用水中PFASs

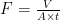
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:X52 文献标志码:A DOI: 10.3969/j .issn.1003-9015.2025.04.020
文章编号:1003-9015(2025)04-0762-11
Abstract:With the progresson of industrialization,an increasing number of emerging contaminants (ECs)have entered natural water bodies.Among these,per-and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFASs)are aparticular classof synthetic compoundscharacterized by their exceptional stability,bioaccumulation potential,and toxicity,posing significant threats to human and ecological health. This study introduced calcium chloride ( CaCl2 )into the aqueous phase to facilitate the chelation between Ca2+ and acyl chloride monomers,thereby internally regulating the interfacial polymerization(IP)reaction.Asaresult,a CaCl2 -modified nanofiltration membrane( CaCl2 -TFC)was succesfully prepared,featuring a thinner,rougher,more hydrophilic surface with enhanced negative charge and a lowermolecular weight cut-off. The impact of CaCl2 concentration on the separation performance of the nanofiltration membrane was investigated. The results indicate that the modified membrane achieves a pure water flux of 101. (204号 86L⋅m-2⋅h-1 ,nearly 3.28 times that of unmodified TFC membrane,with a Na2SO4 rejection rate of 95.61% ,overcomingthe trade-off effct of TFC membranes.This alleviates the trade-offeffect between water permeability and solute rejection to some extent. Furthermore,the membrane exhibites rejection rates of 95.78% and 90.92% for PFHxAandPFHxS,respectively.Thisresearch presents a simple,environmentally friendly,and low-cost method for thefabricationof TFC NF membranes,applying it to the treatmentof PFASsand providing atechnical reference for ensuringdrinking water safety.
Key words:drinking water safety;nanofiltration membrane;thin-film composite;PFASs;trade-off ffect
1前言
自然水体中的新污染物(ECs)已成为危害人体和生态健康的重大要素之一[1]。(剩余16222字)