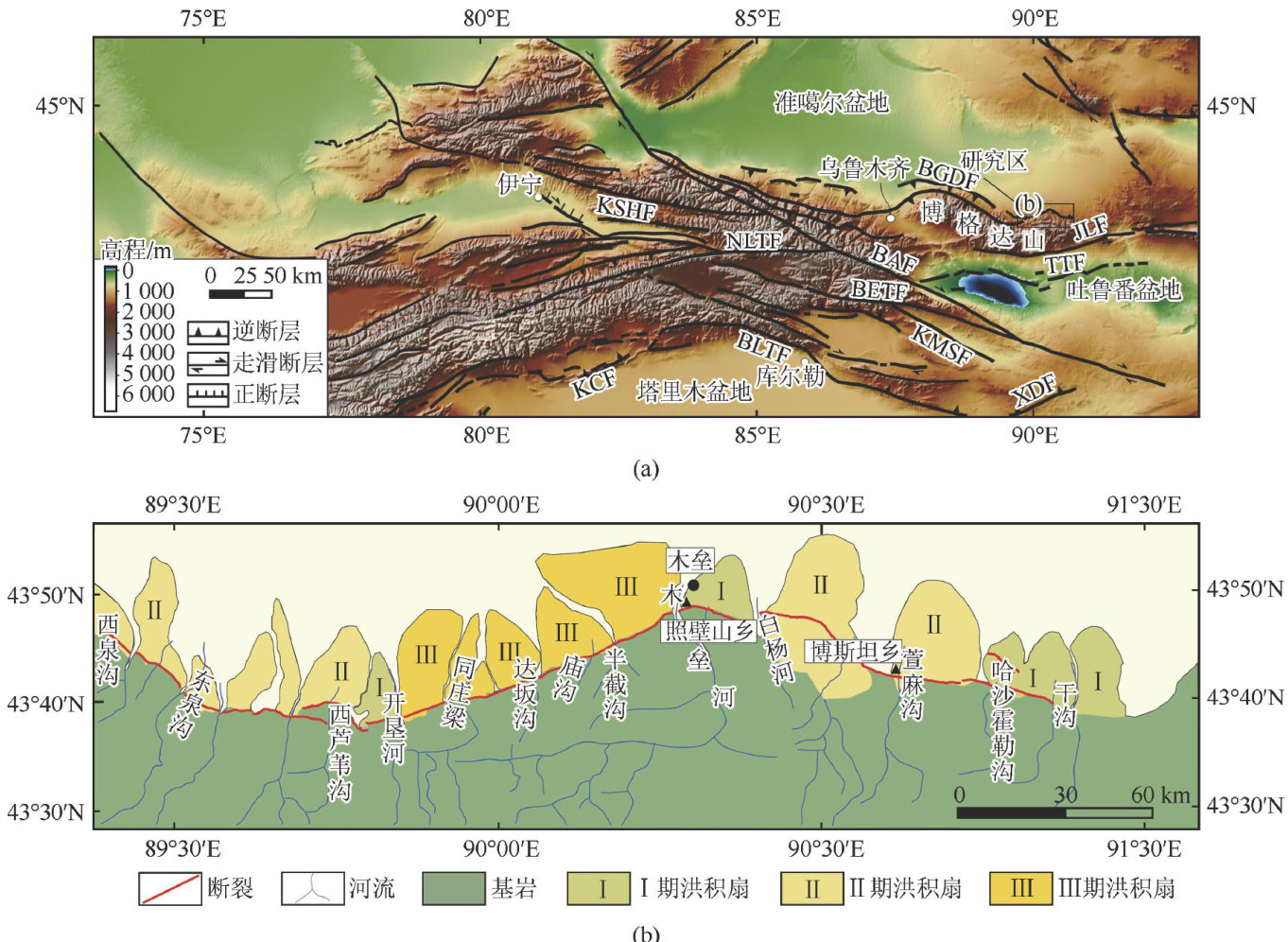
东天山博格达北缘断裂东段晚第四纪活动特征

打开文本图片集
中图分类号:P542.3 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1000-0844(2025)05—1243-08
Abstract: The Bogda Mountains are a major component of the Eastern Tianshan,with the Bogda north margin fault along the northern piedmont serving as the tectonic boundary between the northern Bogda Mountains and Junggar Basin. The western segment (Fukang fault) exhibits intense Late Quaternary activity, but quantitative constraints on the activity characteristics of its eastern segment remain inadequate. To investigate the Late Quaternary activity characteristics of this fault,we conducted geometric and kinematic surveys, measured topographic profiles using digital elevation model data derived from unmanned aerial vehicles,and collected geochronological samples to determine the ages of geomorphic surfaces. The results indicated that the Bogda north margin fault is dominated by north-directed thrust motion with an average vertical slip rate of (0.30±0.04)mm/a during the Late Quaternary. Compared to deformation rates along the western segment of the Northern Tianshan piedmont fault, this reduced activity intensity aligns with the overall west-to-east decrease in deformation rates across the Tianshan orogen.
Keywords: Eastern Tianshan; Bogda northern margin fault; Late Quaternary; slip rate; activity characteristics
0 引言
晚新生代期间印度板块与欧亚板块碰撞的远程效应,导致天山造山带再次活动,发生陆内造山运动并强烈隆升,形成现今的构造格局和地貌形态[1-4]天山地区南北向的地壳缩短速率最大可达 20mm/a 左右[5],这一变形速率主要被天山南北两侧的前陆冲断带所调节和吸收[6-7]。(剩余10722字)