基于斜坡单元和信息量-逻辑回归的滑坡易发性评价
——以三峡库区香溪河与咤溪河流域为例

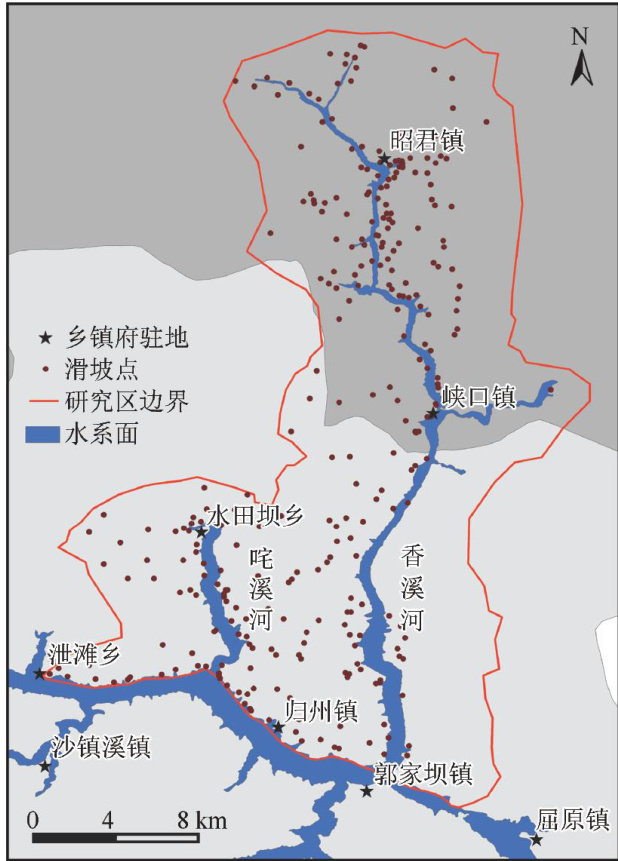
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:P642.22 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1000-0844(2025)05—1090—12
Abstract: Frequent landslides in the Xiangxi and Zhaxi River basins of the Three Gorges Reservoir area pose significant threats to life,property,and transportation safety. To investigate the causes and development of landslides in this area, this study selected 1l influencing factors, namely elevation,elevation difference,slope gradient,slope aspect,engineering geological rock groups, slope structure,water contact degree, distance to water systems, distance to roads, rainfall,and land use. The results showed the following: (1) Rainfall and engineering geological rock groups exhibited the strongest positive correlation with landslide occurrence.(2) Susceptibility patterns differed significantly between the two basins because of geological and lithological variations,i.e.,the right and southern left banks of the Xiangxi River showed higher susceptibility than the northern left bank,whereas both banks of the Zhaxi River exhibited high to very high susceptibility.(3) Susceptibility levels decreased significantly with the increase in distance to rivers; meanwhile,areas with intensive human activities generally exhibited higher susceptibility. The model achieved an accuracy of O.840 under the receiver operating characteristic curve,confirming its reliability in landslide prediction. Slope units exhibited superior alignment with actual landslide distributions compared with grid-based approaches.
Keywords: slope unit; information value; logistic regression; landslide; susceptibility
0 引言
三峡库区于2003年蓄水至今,经过多次周期性的库水位升降,引发了一系列老滑坡复活和新滑坡产生[1]。(剩余15505字)