含冰量分布差异对冻土桩基础承载性能影响的模拟研究

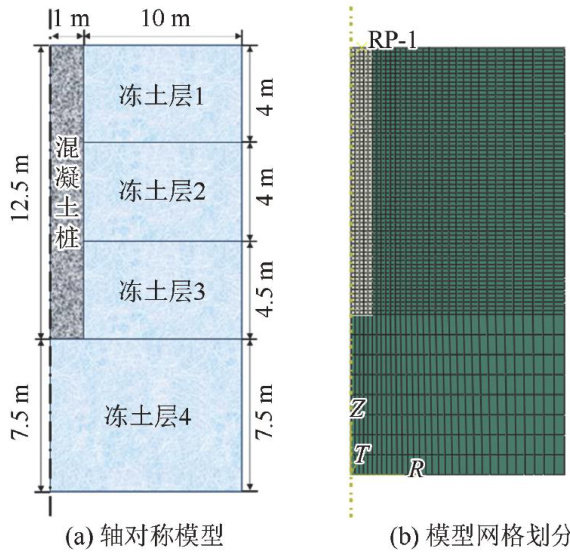
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:P642.14 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1000-0844(2025)05—1120—08
Abstract: This study explores how ice content distribution differences in permafrost around piles affect the bearing performance of pile foundations. Understanding these effects is crucial for pile foundation design,construction,and deformation control in permafrost regions. The finite element software ABAQUS was employed to simulate and calculate the load transfer and bearing capacity of pile foundations under different ice content distribution patterns. Three distinct distribution patterns were defined: inverted trapezoid (ice content decreasing with depth),lanternshaped (ice content initially increasing and then decreasing with depth),and regular trapezoid (ice content increasing with depth).Results indicate that despite identical total ice content around the pile shaft,the bearing performance is considerably affected by ice distribution patterns. At a load of 26MN ,the displacements are 0.026, 0.030 ,and 0.032m for inverted trapezoid,lanternshaped,and regular trapezoid distributions,respectively. Under identical loads,the settlement at the pier top with an inverted trapezoidal ice distribution is smallr than that with a regular trapezoidal distribution,and the lantern-shaped distribution exhibits intermediate settement.Shaft friction exhibits high values in the upper layers and low values in the deeper layers. These findings provide theoretical references for foundation engineering design and construction in cold regions.
Keywords: permafrost; pile foundation; ice content; bearing capacity; finite element analysis
0 引言
桩基础是一种承载能力大、变形小、地质条件适用范围广的基础形式,可以将上部荷载传递至土体深层[1-3]。(剩余14259字)