载镧稻壳炭对废水中磷的吸附性能研究

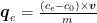
打开文本图片集
中图分类号:X703.1 文献标识码:A
Abstract: With the aceleration of industrialization and increasing water scarcity,phosphorus removal from wastewater has become a critical issue in environmental protection. To address this challenge,this study utilized rice husk to prepare biochar(RCA)and modified it by loading lanthanum via an impregnation method to yield modified biochar (La-RCA). The adsorption performance and mechanisms of lanthanum chloride-modified biochar for phosphorus in wastewater were systematically investigated. Static adsorption experiments were conducted to examine the effects of key parameters (e.g. ,initial solution pH ,adsorbent dosage)on phosphorus adsorption by La-RCA,and the underlying mechanisms were explored. The results demonstrated that: phosphorus adsorption onto La-RCA followed the pseudo-second-order kinetic model, indicating a chemisorption-dominated process. Fitting with the intra-particle diffusion model revealed that the adsorption process was jointly controlled by surface adsorption and intra-particle diffusion. The Langmuir equation provided an excellent fit for the adsorption behavior,suggesting that monolayer adsorption was the primary mechanism. The optimal initial pH range for phosphorus adsorption was 3. 0-8.0 ,demonstrating strong acid-base tolerance of La-RCA. The optimum adsorbent dosage was 0.4g/L ,achieving near-complete removal of phosphate from solution. Characterization analyses (FT-IR,XRD,XPS)confirmed that electrostatic attraction and ligand exchange were the dominant adsorption mechanisms. These findings indicate that the development of lanthanum-loaded rice husk biochar not only provides a novel approach for the resource utilization of agricultural waste but also offers an eficient and cost-effective solution for phosphorus removal from wastewater.
Key words: rice husk biochar; lanthanum;phosphate; static adsorption
随着全球农业和工业科技的发展,水体富营养化已经成为一个不容忽视的问题。(剩余11984字)