攀枝花市碳排放脱钩效应及其驱动因素分析

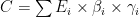
打开文本图片集
DOI: 10. 13718/j. cnki. xdzk. 2025. 10.012
中图分类号:X321 文献标识码:A文章编号:1673-9868(2025)10-0134-11
Abstract:To explore the decoupling relationship between carbon emissions and economic growth in Panzhihua City,aiming to achieve coordinated progress in carbon reduction and economic development,we combined the Tapio model with the LMDI factor decomposition method to analyze the decoupling characteristics of carbon emissions and economic growth in Panzhihua from 20o7 to 2O22,along with the impact of driving factors on this relationship. The results indicate that: ① Over the past 16 years,Panzhihua's average carbon emissions were 1837.37×104t ,with emissions rising from 2007 to 2011,stabilizing from 2012 to 2014,and declining from 2015 to 2022. Carbon emission intensity decreased from 4.80 t/ten thousand yuan to 1.06t/ ten thousand yuan. ② In Panzhihua,raw coal accounted for 55.68% of carbon emissions, followed by cleaned coal (25.06% )and coke (16.72% ),while total emissions from electricity, diesel,gasoline,and kerosene were less than 5% : ③ The decoupling state of carbon emissions in Panzhihua from 2Oo8 to 2O14 was unstable,exhibiting three alternating states:weak decoupling,expansionary negative decoupling,and strong decoupling. From 2015 to 2022,the state concentrated on strong decoupling. ④ The energy intensity effect primarily restrains the carbon emissions and promotes the decoupling of emissions from economic growth in Panzhihua,while the economic level effect promotes the emissions and hinders the decoupling. In the future,the energy structure effect and population size effect are expected to become significant factors promoting decoupling. Therefore,to achieve low-carbon development and meet the "double carbon" goals, Panzhihua should focus on continuously adjusting its energy structure, optimizing and upgrading traditional industries,and enhancing talent development and introduction.
Key words: Tapio decoupling model; LMDI factorization; carbon emissions; economic growth; PanzhihuaCity
工业革命以来,人类社会在快速发展的同时也在加剧对自然资源的攫取,尤其是对化石能源的粗放式利用,导致二氧化碳等温室气体的排放量急剧增加[]。(剩余11318字)